Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Rodent paleocommunities from Ulantatal
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
L'occlusion dentaire chez Peradectes, Amphiperatherium et Peratherium, Marsupiaux du tertiaire d'Europe.Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Didelphidae; Eocene; Mastication; Oligocene; Wear facetsAbstract The general principles guiding the study of wear facets which develop during mastication in mammals possessing tribosphenic molars are named. The application of this method of study to the molars of European Tertiary Didelphidae shows that the lineage of this family as represented by the species Peratherium cuvieri (Upper Eocene), P. elegans (Lower-middle Oligocene) and P. antiquum (Upper Oligocene) has propessively evolved toward a more carnivorous diet. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
Les oiseaux aquatiques (Gaviiformes à Anseriformes) du gisement Aquitanien de Saint-Gerand-le-Puy (Allier, France): Révision systématique.Jacques ChenevalKeywords: Aves; Early Miocene; Osteology; Palaeoecology; SystematicsAbstract Six orders of birds adapted to aquatic life are represented among the numerous avifauna of "Saint-Gérand-le-Puy": Gaviiformes, Procellariiformes, Pelecaniformes, Ciconiiformes, Phoenicopteriformes, and Anseriformes. The present study of this avifauna proposes several changes in systematics:- Procellariiformes: Puffinus arvernensis does not belong in Procellariidae but in Diomodeidae, and it is transferred to the fossil genus Plotornis previously described in the Middle Miocene of France. - Pelecaniformes: Phalacrocorax littoralis remains in Phalacrocoracidae; P. míocaenus is different from the modern species, and is transferred to the new genus Nectornis. Empheresula arvernensis, described in the Oligocene deposits of Gannat, seems to be present in Saint-Gérand-le-Puy too. Pelecanus gracilis shows many differences from the modern species, and belongs to the new genus Miopelecanus, - Ciconiiformes: Ardea formosa nom. oblit. is a synonym of Proardeola walkeri. - Anseriformes: a new species closely related to swans is described, and belongs to the fossil genus Cygnopterus, of the Middle Oligocene of Europe; this species is called C. alphonsi. The ecology of each species is suggested by comparison with that of its nearest living relatives, and by study of osteological adaptations. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Fasc. 2 (1984) |
|
|
|
Les rongeurs du site Pliocène à Hominidés de Hadar (Ethiope)Maurice SabatierKeywords: Ethiopia; hominids; Muridae; PlioceneAbstract The intensive exploration of the Pliocene Hadar Formation, rich in hominid remains, led us to the discovery of several micromammals levels. ln some of them, rodents are very abundant. The stratigraphic repartition of these levels do not cover the whole fossiliferous series of the formation but takes place only in the sedimentary members from Sidi Hakoma and Denen-Dora (rancing from 3.1 - 3.2 MY to 2.8 - 2.9 MY, according to the recent geochronological data). During this gap of time, the species do not show morphological changes, what allowed us to gather, in the same taxa, forms of slighty different ages. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 1 (1982) |
|
|
|
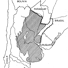
Mammals and stratigraphy of the continental mammal-bearing Quarternary of South AmericaLarry G. Marshall, Annalisa Berta, Robert Hoffstetter, Rosendo Pascual, Osvaldo A. Reig, Miguel Bombin and Alvaro MonesKeywords: Geochronology; Mammalia; Quaternary; South America; StratigraphyAbstract Previous chronological arrangements of South American Quaternary land mammal faunas are appraised on the basis of current geological and paleontological data. Three South American late Pliocene-Pleistocene land mammal ages are conventionally recognized, from oldest to youngest, the Uquian, Ensenadan, and Lujanian ; all are defined on Argentine faunas. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Ext (1984) |
|
|
|
Decouverte d'un nouveau Diacodexis (Artiocactyla, Mammalia) dans l'Eocène inférieur de Silveirinha, Portugal.Carmen Estravis and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Artiodactyla; Eocene; Migration; Portugal; SilveirinhaAbstract A new artiodactyl, Diacodexis antunesi n.sp., is described from the early Eocene of Silveirinha, Portugal. Comparisons are made with Diacodexis gazini GODINOT, 1978, D. varleti SUDRE et al., 1983, D. cf. varleti from Paris Basin sites, D. sp. from Dormaal and from localities in Spain and England, D. secans from North America and D. pakistanensis from Asia; affinities and evolutive tendencies are discussed. The presence of Diacodexis in the locality of Silveirinha confirms the very early Eocene age of the latter. As Diacodexis antunesi appears ta be more primitive than D. gazini from Rians (early Eocene of France), it lends corroboration to the interpretation (essentially based previously on condylarths) of the Silveirinha assemblage as the oldest Eocene fauna known in Europe and supports the hypothesis that early artiodactyls migrated from Europe to North America. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|

|
Première occurrence d'un mégachiroptère ptéropodidé dans le Miocène moyen d'Europe (Gisement de Lo Fournas-II, Pyrénées-Orientales, France).Jean-Pierre Aguilar, Marc Calvet, Jean-Yves Crochet, Serge Legendre, Jacques Michaux and Bernard SigéKeywords: Europe; First occurence; Megachiroptera; Middle Miocene; TeethAbstract A lot of isolated teeth of a pteropodid fruit bat has been recently found within an assemblage of micromammals recovered from a karstic fissure filling named Lo Fournas-Il near the locality of Baixas (Pyrénées-Orientales, France). The fauna is Middle Miocene Serravallian age. The fossil fruit bat appears morphologically close to Rousettus; its size is that of a recent medium-sized fruit bat. While the fruit bats are very poorly known as fossils, this discovery shows that one of their recent types of dentitions was perfectly established by Middle Miocene times, and supports the presumed long geologic story of the suborder. One of the major invasions of the Old World fruit bats, supposed originated from SE Asia, reached up to Europe. A suborder unit is added to the miocene fauna of this continent. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 3 (1986) |
|
|
|
Une faune du niveau d'Egerkinger (MP 14; Bartonien inférieur) dans les phosphorites du Quercy (Sud de la France)Jean Sudre, Bernard Sigé, Jean-Albert Remy, Bernard Marandat, Jean-Louis Hartenberger, Marc Godinot and Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Biochronology; Early Bartonian; Eocene; evolution; Mammals; New taxa; QuercyAbstract The Laprade fauna is chronologically situated between those from Egerkingen and Lissieu and consequently, is close to the MP 14 reference-level of the European mammalian biochronological scale (Symposium of Mainz, 1987). Article infos Published in Vol. 20, Fasc. 1 (1990) |
|
|

|
La Poche à phosphate de Ste-Neboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien Supérieur. 3- ChéloniensFrance de BroinKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The few remains recently collected at Ste Néboule (upper Eocene) belong to three genera: the Testudinid Ergilemys, of which it is the oldest occurence in Western Europa, probably Palaeochelys and an unpublished genus, which is peculiar to the Phosphorites du Quercy. Some statements are made on the chelonian fauna as a whole in that région. After the study of some characters proper to the genus Ergilemys, some remarks are made concerning its antecedents and descendants. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Henri Menu, 1925-2007Bernard SigéKeywords: bats; biographydoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.1-5 Abstract Record of life and works of Henri Menu, French zoologist, contributor to the knowledge of living and fossil bats. Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|

|
Eléments nouveaux sur l'évolution des genres Eucricetodon et Pseudocricetodon (Eucricetodontinae, Rodentia,Mammalia, de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Bernard ComteKeywords: evolution; Occidental Europe; Oligocene; Rodentia; SystematicsAbstract The review of material recently collected in the new localities from the “Phosphorites du Quercy", and different localities from the South of France, bring new informations on the genus Eucricetodon THALER. 1966, and Pseudocricetodon THALER, I969 (Middle and Upper Oligocene. Western Europe). Thanks to Eucricetodon huerzeleri VIANEY-LIAUD, 1972, which were unsufficiently known until now, is proposed. During the middle Oligocene Eucricetodon atavus MISONNE, 1957 seems to give rise to two lineages. One of them led to Eucricetodon huberi,which however exhibits a larger size and a development of progressive characters on the teeth. The other would be Eucricetodon huerzeleri well differentiated at the “Mas de Pauffié" standard level (beginning of the upper Oligocene). The ornementation of lower incisors is described, when possible. Though the fossils are not abundant, it seems that the ancestral lineage, Eucriretodon atavus, remains in the upper Oligocene (Boningen standard level). evolving into Eucricetodon praecursor SCHAUB, 1925 (Rickenbach standard level). The characters of Eucricetodon dubius (SCHAUB. 1925), represented by a numerous population in Pech Desse and Pech du Fraysse (Quercy). confirm that this species and Eucricetodon praecursor belong to two different lineages. As Eucricetodon dubius shows more primitive features, this species could not originale from Eucricetodon atavus -Eucricetodon huberi. The appearance of this species at the level of Mas de Pauffié could be the result of an immigration. A new definition of Pseudocricetodon incertus (SCHLOSSER. 1884) is given. This species has been found in several localities, where it had not been identified until now. lts comparison with Pseudocricetodon moguntiacus (BAHLO. l975), found at several localities from the standard level of Antoingt (end of middle Oligocene). shows a parallel evolution to that of Pseudocetodon incertus, which is of larger size and with a less complicated pattern of teeth. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 1 (1985) |
|
|
|
Deux nouveaux primates dans l'Oligocène inférieur de Taqah (Sultanat d'Oman): premiers Adapiformes (?Anchomomyini) de la péninsule arabique?Emmanuel Gheerbrant, Herbert Thomas, Jack . Roger, Sevket Sen and Zaher Al-SulaimaniKeywords: Adapids; Afro-Arabian plate; Early Oligocene; New taxa; Primates; Trans-Tethyan dispersalsAbstract Two new species, Omanodon minor n. g., n. sp. and Shizarodon dhofarensis n. g., n. sp., known from fifteen isolated teeth, are described here as the first adapiform primates (?Anchomomyini) recognizable to date in the Taqah material (early Oligocene of Sultanate of Oman). Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 4 (1993) |
|
|
|
Leptacodon nascimentoi n,sp., un nouveau Nyctitheriidae (Mammalia,Lipotyphla) de l'Eocène inférieur de Silveirinha (Baixo Mondego, Portugal)Carmen EstravisKeywords: Eocene; Leptacodon; Lipotyphla; Mammals; Nyctitheriidae; Portugal; SilveirinhaAbstract In this article is described a new species of Nyctitheriidae with primitive characters: Leptacodon nascimentoi n. sp. from the early Eocene of Silveirinha (Portugal). Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
Middle Eocene rodents from the Subathu group, Northwest Himalya.Kishor Kumar, Rahul Srivastava and Ashok SahniKeywords: Chapattimyidae; Eocene; evolution; India; Rodentia; Subathu group; SystematicsAbstract Extensive collecting in previously known and new Middle Eocene rodent localities in the Subathu Group of the Rajauri and Reasi districts, Jammu and Kashmir (northwest Himalaya, India) has yielded over 500 isolated cheek teeth, numerous incisors and cheek tooth fragments, and two mandibular fragments with M/1-M/3. An analysis of this additional material and a restudy of that reported earlier from the Metka (Rajauri) area has revealed the presence of diverse Middle Eocene ctenodactyloid rodents in India. The assemblage comprises six genera and twelve species, viz.., Bírbalomys woodi, B. ibrahimshahi, B. sondaari, Basalomys vandermeuleni, B. ijlsti, B. lavocati, Chapattimys wilsoni, C. debruijni, Gumbatomys asifi, cf. Advenimus bohlini, cf. Petrokoslovia sp. indet. 1 and cf. Petrokoslovia sp. indet. 2. Most species of this assemblage are endemic to the Indian subcontinent and are referred to the Family Chapattimyidae. However, at least three taxa, viz.., cf. Advenimus bohlini, cf. Petrokoslovia sp.indet. 1 and cf. Pezrokoslovia sp. indet. 2 show close affinities with their Central and Eastern Asiatic contemporaries and are attributed to the Family Yuomyidae. The dentitions of most of the Middle Eocene rodents from India are described here in better detail thus providing more precise characterization than was available earlier. The taxonomie status of Basalomys, formerly a subgenus of Birbalomys has been raised to that of a genus. Basalomys vandermeuleni is here designated as the type species of Basalomys in place of B. ijlsti. The rodent assemblage from the Subathu Group is specifically similar to that from the coeval Kuldana Formation of Pakistan. The absence of Birbalomys ibrahimshahi and cf. Advenimus bohlini in Pakistan is related to sampling bias. The identifications of the Early Eocene rodents from Barbara Banda, Pakistan have been reexamined and the familial assignments of some of the Early and Middle Eocene rodents from Central and Eastern Asia have been discussed and reviewed in the light of recent discovery of early rodents in Mongolia. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|

|
THE ANIMALS Systematische ZoologieLeigh M. Van ValenKeywords: Book review; SystematicsAbstract Systematische Zoologie by A. REMANE, V. STORCH, and U. WELSCH. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 1 (1986) |
|
|
|
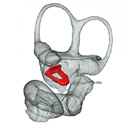
Fallen in a dead ear: intralabyrinthine preservation of stapes in fossil artiodactylsMaeva J. Orliac and Guillaume BilletKeywords: allometry; bony labyrinth; inner ear; middle ear ossiclesdoi: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e3 Abstract The stapes is the last of the middle ear ossicle chain and the smallest bone of the mammalian skeleton. Because it rests on the membrane of the fenestra vestibuli during life, the stapes may often fall within the bony labyrinth cavity when soft structures decay after death. In this work, we highlight the unexpected role that the bony labyrinth plays in the preservation of the stapes. Systematic investigation of the bony labyrinth of 50 petrosal bones of extinct and extant artiodactyls led to the discovery of eight cases of “intralabyrinthine” stapes. Three dimensional reconstructions of these stapes allow documenting stapes morphology of four extinct artiodactyl taxa: Microstonyx erymanthius (Suidae), Elomeryx borbonicus (Hippopotamoidea), ?Helohyus plicodon (Helohyidae), and an undetermined Cainotheriidae; and four extant ones Choeropsis and Hippopotamus (Hippopotamidae), and Tayassu and Phacochoerus (Suoidea). ?Helohyus plicodon from the Middle Eocene documents the oldest stapes known for the order Artiodactyla. Morphological study and metric analyses of our sample of artiodactylan stapes show that stapes are likely to carry relevant phylogenetic characters/signal within artiodactyls, and a potential Euungulata signature. Article infos Published in Vol.40-1 (2016) |
|
S.I. Data |

|
A new species of bat (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) from the early Oligocene global cooling period, Brule Formation, North Dakota, USANicholas Czaplewski, Jeff Person, Clint Boyd and Robert EmryKeywords: Eocene-Oligocene global cooling; Mammalia; Oligocene; Plecotini; Quinetiadoi: 10.18563/pv.42.2.e2 Abstract We report the first confirmed fossil bats from North Dakota, including a new species referable to the Vespertilionidae represented by a maxilla with P4-M3 from the Brule Formation, Fitterer Ranch local fauna, early Oligocene, Whitneyan North American Land Mammal Age. Unassociated postcranial fragments of the humerus and femur also represent a vespertilionoid, but appear to reflect a different, unidentified species. The new taxon, Quinetia frigidaria sp. nov., is referred to the genus Quinetia, previously known only from approximately contemporaneous deposits in Europe. The new species is larger than Quinetia misonnei from the early Oligocene of Belgium. It is similar in some morphological characters to Chadronycteris rabenae (Chiroptera incertae sedis) of the late Eocene (Chadronian) of northwestern Nebraska and to Stehlinia species (?Palaeochiropterygidae) from the Eocene and Oligocene of Europe, but differs from each in morphological details of the dentition and maxilla. An unassociated talonid of a lower molar from Fitterer Ranch shows myotodont morphology, unlike the nyctalodont lower molars in Q. misonnei, and thus represents a second chiropteran taxon in the fauna. Quinetia frigidaria is a member of a Paleogene radiation of bats near the low point of the Eocene-early Oligocene decline in global temperatures, increased seasonal aridity, and loss of tropical floras from mid-latitude North America. Article infos Published in Vol 42-2 (2019) |
|
|
|
Latest Early-early Middle Eocene deposits of Algeria (Glib Zegdou, HGL50), yield the richest and most diverse fauna of amphibians and squamate reptiles from the Palaeogene of AfricaJean-Claude Rage, Mohamed Adaci, Mustapha Bensalah, Mahammed Mahboubi, Laurent Marivaux, Fateh Mebrouk and Rodolphe TabuceKeywords: Africa; Algeria; amphibians; Eocene; squamatesdoi: 10.18563/pv.44.1.e1 Abstract HGL50 is a latest Early-early Middle Eocene vertebrate-bearing locality located in Western Algeria. It has produced the richest and most diverse fauna of amphibians and squamate reptiles reported from the Palaeogene of Africa. Moreover, it is one of the rare faunas including amphibians and squamates known from the period of isolation of Africa. The assemblage comprises 17 to 20 taxa (one gymnophionan, one probable caudate, three to six anurans, seven ‘lizards’, and five snakes). Two new taxa were recovered: the anuran Rocekophryne ornata gen. et sp. nov. and the snake Afrotortrix draaensis gen. et sp. nov. The locality has also yielded the first confirmed anilioid snake, the first Palaeogene gymnophionan, and probably the first caudate from the Palaeogene (and possibly from the Tertiary) of Africa. The presence of a caudate at that time in Africa would be of particular interest; unfortunately, the available material does not permit a definitive identification. The fauna comprises Gondwanan and more specifically West Gondwanan vicariants, probably autochthonous groups and a Eurasian immigrant (assuming that the identification of the caudate is accurate). The fauna from HGL50 is clearly distinguished from the few other Eocene assemblages of Africa. However, if this results largely from differences in geological ages, geographic positions of the localities and mainly differences in environments took a part in the composition of the faunas. Article infos Published in 44-1 (2021) |
|
|

|
Les Bovidae (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) du Miocène moyen de la formation Hofuf (Province du Hasa, Arabie Saoudite).Herbert ThomasKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Bovidae; Middle Miocene; Palaeogeography; Saudi ArabiaAbstract The study of the bovids from Al Jadidah (Hofuf Formation, Saudi Arabia) confirms that the fauna comes from a pre-Hipparion level. The Al Jadidah age is close to that of Fort Ternan (14 m.y.) and Beni Mellal, but cannot be older than that of Fort Ternan. The age of the Hofuf Formation is close to but slightly older than the oldest deposits of the Ngorora Formation (Kenya). 7 to 9 species have been recorded, of which 2 to 4 remain indeterminate. If the great specific diversity of te bovids from this locality gives evidence of immigrations from anterior Asia (Turkey) (e.g. Pachytragus Iigabuei sp. nov.), the bovid assemblage of Al Jadidah results in fact from a double influence: from the anterior Asia and mainly from Africa (e.g. the Caprotragoides lineage and the Neotragini? Homoiodorcas). The Al Jadidah bovids reflect, on the whole, the predominant character of open to very open environment, which supports the conclusions drawn from our two preliminary studies. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 5 (1983) |
|
|

|
Pseudorhyncocyon cayluxi Filhol, 1892 insectivore géant des phosphorites du QuercyBernard SigéKeywords: Insectivores; Leptictidae; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Une hémimandibule et une molaire supérieure recueillies dans le gisement oligocène inférieur d'Escamps (phosphorites du Quercy) fournissent de nouvelles informations sur le genre Pseudorhyncocyon FllHOL, grand insectivore longirostre du Paléogène d'Europe, fossile très mal connu jusqu'ici. Des comparaisons avec les macroscélididés africains, géolabididés nord-américains, et leptictidés euraméricains permettent de rattacher cet amimal aux leptictidés, et de le rapprocher du genre Lepticidium TOBIEN, au sein de la sous-famille européenne nouvelle des pseudorhyncocyoninés. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 2 - les carnivoresGérard de BeaumontKeywords: anatomy; Carnivora; France; Montredon; Systematics; Upper MioceneAbstract The locality of Montredon has provided 8 species of camivores, often little documented, that are discribed and depicted. All the remains are fragmentary and generally badly preserved which lowers very much the possible precision of the taxonomic study; this one has however allowed the creation of a new subspecies. The most richlypdocumented forms are an ursid (Indarctos) and a felid (Machairodus). Issuing often from a westem Europe evolution, the carnivores are well inserted between those of the better known faunas of the "Classical Pontian" and of the lower Vallesian and this situation fits also well with their stratigraphic level, that cannot however be more accurately defined with them alone. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|