Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Rodent paleocommunities from Ulantatal
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
First evidence of an early Miocene marine teleostean fish fauna (otoliths) from la Paillade.(Montpellier,France)Bettina Reichenbacher and Henri CappettaKeywords: Aquitanian; Biostratigraphy; La Paillade; marine deposits; Miocene; otoliths; Palaeoecology; Palaeogeography; Southern France; TeleosteiAbstract A fossil fish fauna, based on 5533 otoliths, from the La Paillade locality at Montpellier is described and figured. The otolith-bearing marls correlate to mammal zone MN l (Aguilar, 1982), and thus represent the earliest Miocene. The fish fauna consists of 30 taxa belonging to 20 families. Two species are new: Dussumieria sittigi and Liza gaudanti. The predominant faunal element is the Lesueurigobius vicínalis-species complex, composing 73% of all investigated otoliths. The palaeoecological analysis reveals a marine to euryhaline fish fauna living under tropical to subtropical conditions in the transition zone littoral - sublittoral. Water depth probably was more than 10 m. The scarcity of pelagic físhes suggests that the habitat was either a sheltered bay and/or far away from the open sea. Furthermore, some genera represented in the La Paillade fish fauna presently live exclusively in the Indopacific realm. Their presence strongly supports a broad connection between the Indian Ocean, the Mediterranean, and the Paratethys Seas during the Early Miocene (Aquitanian). From a palaeobiogeographical point of view, faunal relationships were found between the La Paillade fish fauna and both the Paratethys fish fauna and the fish fauna from the deposits in the Upper Rhinegraben and the Mayence and Hanau Basins (Germany). Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 1 (1999) |
|
|

|
Les mammifères Montiens de Hainin (Paléocène moyen de Belgique) Part1: Multituberculés.Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Belgium; Hainin; Mammals; multituberculates; PaleoceneAbstract The Montian locality of Hainin (Hainaut, Belgium) yielded about twenty teeth of Multituberculates. They are very peculiar forms, showing no affinities, at the generic level, with those hitherto known from North America, Asia and Europe. They are referred to the new taxa Boffius splendidus nov. gen., nov. sp., Hainina belgica nov. gen., nov. sp., and H. godfriauxi nov. gen., nov. sp. They expose some common features, such as the advanced type of first upper molar. possessing at least three complete rows of cusps. Because of this, and also of the upper premolar reduction, Boffius splendidus appears as the most specialized form within the Ptilodontoidea suborder. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 4 (1979) |
|
|

|
Avant-proposMarc Godinot and Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: D.E.RussellAbstract Le présent volume est l'aboutissement d'un projet né il y a presque cinq ans. En décembre 1991, l'un d'entre nous (MG) prenait des contacts en vue de proposer un symposium sur les mammifères fossiles, dédié à D.E. Russell, dans le programme du 4e Congrès de la European Society for Evolutionary Biology. Ce congrès, baptisé "Evolution 93", devait se tenir à Montpellier en août 1993. Son Comité d'Organisation, animé par F. Catzeflis, recherchait des organisateurs de symposiums. L'idée fut acceptée avec enthousiasme par le second d'entre nous (PDG), et le titre de notre Symposium fut précisé: " Palaeobiology and Evolution of Early Cenozoic Mammals - A Symposium in Honor of D.E. Russell". Le projet fut formellement accepté par le Comité d'Organisation en avril 1992. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
Mammals and stratigraphy : the Paleocene of EuropeDonald E. Russell, Jean-Louis Hartenberger, Charles Pomerol, Sevket Sen, Norbert Schmidt-Kittler and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Europe; Mammalia; Mammalian biochronology; Paléogène; StratigraphyAbstract The mammalian faunas of the Paleogene of Europe and their localities are reviewed with comments on problems of European stratigraphy (epoch, stage and substage limits) and on the possibilities of faunal migrations. Radiometric dating is discussed. A stratigraphic scale for the Paleogene is presented, as well as a refined system of sequential faunal levels. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Ext (1982) |
|
|
|
Les serpents des phosphorites du QuercyJean-Claude RageKeywords: Grande Coupure; Quercy Phosphorites; SerpentsAbstract A short review of the genera and species of snakes from the Quercy's phosphorites described by former authors is followed by the study of specimens recently collected. Most of these latter specimens belong to the Aniliidae, Boidae, Colubridae and to the Scolecophidia; the precise systematic position of some of them is not defined yet. The following genera and species are described: Eonilius europae nov. gen. and nov. sp., Platyspondylia lepta nov. gen. and nov. sp., Coluber cadurci nov. sp. and Dunnophis cadurcensis nov. sp.; a species described by de Rochebrune (Palaeopython filholi) is revised. One of the most important conclusions of this study is that the Colubridae appear as early as the Upper Eocene. The stratigraphic repartition of these snakes shows that the rich Upper Eocene fauna is followed by the very reduced fauna of the Lower Oligocene; then the oligocene «Grande Coupure» corresponds to a very important faunistic renewal. The fauna remains poor and little diversified during the beginning of the Middle Oligocene after which there is a new faunistic explosion. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|

|
The new Algerian locality of Bir el Ater 3: validity of Libycosaurus algeriensis (Mammalia, Hippopotamoidea) and the age of the Nementcha FormationFabrice Lihoreau, Lionel Hautier and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Dispersal event; Miocene; North Africa; Tetralophodondoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e1 Abstract The description of original material of anthracothere and proboscidean in the new locality of Bir el Ater 3 from East Algeria, and a thorough review of early Libycosaurus remains of Bir el Ater 2 allows us validating L. algeriensis as the smallest and earliest species of Libycosaurus and probably the earliest migrant of the genus from Asia. The presence of a Tetralophodon in the Neogene Nementcha formation might represent the earliest occurrence of the genus in Africa. These original fossil remains allow us to discuss the age of the Neogene part of the Nementcha formation close to the Serravalian/Tortonian boundary. Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|

|
Les sélaciens du Miocène de la région de MontpellierHenri CappettaKeywords: Ichtyofauna; Miocene; Montpellierdoi: 10.18563/pv.3.ext.1-139 Abstract The utilization of screen-washing and attack by dilute acetic acid has permitted the collecting, in the Miocene of the department of Hérault (France), of a very rich ichthyofauna. This fauna is presently comprised of about 60 studied species, of which 11 are new, and represents, in the present state of knowledge, the most varied Miocene selachian fauna described in the world. Article infos Published in Vol. 3, Ext (1970) |
|
|
|
The Quaternary avifauna of Crete, Greece.Peter D. WeesieKeywords: Avifauna; Crete; Quaternary; SystematicsAbstract Pleistocene bird fossils have been studied from nine localities on Crete. Part of this material was described earlier by the author (Weesie, 1982) and will not be treated here in extenso, the results will be incorporated. More than one third of the over 10,000 fossil bird bones available could be identified ; they were found to represent at least 65 bird species. The following species of the Pleistocene Cretan avifauna are new to the fauna of Crete : Branta ruficollis, Haliaeetus albicilla, Gyps melitensis, Aquila chrysaetos simurgh n. ssp., Ketupa zeylomensis, Aegolius funereus, Dendrocopos leucotos, Zoothera dauma, Turdus iliacus and Pyrrhula pyrrhula. The Pleistocene Cretan avifauna differs less from comparable mainland avifaunas than (fossil) avifaunas from oceanic islands do. Still, the Pleistocene Cretan avifauna has two qualities that are characteristic of island avifaunas : the almost complete absence of a group of birds (the Galliformes) and the presence of two endemic (sub)species : the giant eagle Aquila chrysaetos simurgh n. ssp. and the long-legged owl Athene cretensis (Weesie, 1982). The new subspecies is described in the present study. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Fasc. 1 (1988) |
|
|
|
Artiodactyla aus den Eozänen Braunkohlen des Geiseltales bei Halle (DDR)Jorg Erfurt and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Artiodactyles; Eocene; Europe; Paleoecology; Stratigraphy; taxonomyAbstract The present study of Artiodactyla from the Middle Eocene of the Geiseltal lignite beds concems systematics, biostratigraphy, and palaeoecology on the basis of 174 specimens: isolated remains to more complete skeletons. Instead of the formerly known five species of two families are now recognized 14 species of the Diacodexeidae, Dichobunidae, Cebochoeridae, and Haplobunodontidae. New species are Aumelasia maniai, Anthracobunodon neumarkensis, Masillabune franzeni. Four species of the Geiseltalfauna are definitely known from elswere, and five species are closely related to those from other European localities. Evidently the faunal situation of artiodactyls during the Middle Eocene of Europe was largely uniform. The distribution of artiodactyls within the sequence of the Geiseltal strata corroborates the biostratigraphical concept of the land mammal age Geiseltalian (Franzen & Haubold l986b) as well as the mammalian reference levels MP 11-13 (Franzen 1987). Reconstructions of the skulls and skeletons allow conclusions on the functional morphology and palaeoecology of the artiodactyls of the European Middle Eocene Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|
|
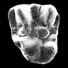
|
Mammifères nouveaux de l'Ilerdien des Corbières et du Minervois (Bas-Languedoc, France)Bernard MarandatKeywords: Bas-Languedoc; Early Eocene; France; Ilerdian; Mammals; New taxaAbstract Four new taxa (two genera, one subgenus, and four species) conceming the orders Condylarthra, Rodentia, Pantolesta, and an undetermined order from middle and middle/upper Ilerdian localities (lower Ypresian) of the Corbières and Minervois regions (Bas-Languedoc, Southem France) are presented in this short paper Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|
|
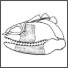
|
Description des restes d'Elasmobranches (Pisces) du Dévonien moyen de BoliviePhilippe JanvierKeywords: South AmericaAbstract Some fragmentary remains of spines and endoskeletal elements, referred here to as ctenacanthid like elasmobranchs, are recorded in the Middle Devonian of Bolivia. These specimens, and some others from the Eodevonian of Brasil represent the only Devonian fish remains hitherto known from South America and indicate that further discoveries may be made in their original localities respectively. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 4 (1977) |
|
|

|
Terrestrial vertebrate paleocommunities from the Cerro del Pueblo Formation (Late Cretaceous; Late Campanian) at Las Aguilas, Coahuila, MexicoHéctor E. Rivera-Sylva, Eberhard Frey, Wolfgang . Stinnesbeck, Natalia Amezcua Torres and Diana Flores HuertaKeywords: Campanian; Coahuila; dinosaurs; Mexico.; Vertebratesdoi: 10.18563/pv.42.2.e1 Abstract The Las Águilas site near Porvenir de Jalpa, Coahuila, Mexico, is extremely rich in tetrapod remains comprising both bones and trackways of several dinosaur taxa of late Campanian age. Within a 50 m thick section we identified at least nine layers with dinosaur bone assemblages. In one of these the dinosaur bones are associated with remnants of eusuchian crocodilians, turtles, plesiosaurs, pterosaurs, tyrannosaurids, dromaeosaurids, parksosaurid, hadrosaurids, ceratopsids, and ankylosaurs. This layer is also rich in coprolites of turtles, crocodilians and likely theropods, thus providing evidence for the wealth of Late Cretaceous vertebrate life in the area. Article infos Published in Vol 42-2 (2019) |
|
|
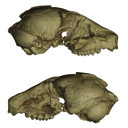
|
The digital endocast of Necrolemur antiquusArianna Harrington, Gabriel Yapuncich and Doug BoyerKeywords: brain evolution; Eocene; Omomyiforms; Primatesdoi: 10.18563/pv.43.2.e1 Abstract The study of endocasts, or casts of the endocranial space, have played an important role in shaping understanding of mammalian, and particularly primate, brain evolution. Recently, the reconstructions of three-dimensional virtual endocasts from high-resolution computed tomography images have allowed for the visualization and quantification of endocasts in several Paleocene and Eocene primate species. Here we present the virtual endocast of MaPhQ 289 (informally known as the Montauban 9 skull), a specimen of Necrolemur antiquus Filhol 1873, a middle to late Eocene European primate of the family Microchoeridae. The virtual endocast of MaPhQ 289 reveals a lissencephalic surface morphology with expanded temporal poles and minimal overlap of the cerebellum or olfactory bulb by the cerebrum, which closely resembles the morphology of the endocast of its contemporary relative, Microchoerus erinaceus (Primates, Microchoeridae). MaPhQ 289 yields an endocranial volume (ECV) of 2.36 cm3, about 60% smaller than the volume of the most commonly cited ECV of N. antiquus. Thus, the size of the brain of N. antiquus relative to its body size is likely to be smaller than has been reported in previous literature, highlighting the importance of corroborating older ECV estimates with new evidence using 3-D imaging techniques. Related dataset Article infos Published in 43-2 (2020) |
|
|
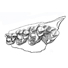
|
Cryptomerix Schlosser, 1886, Tragulidé de l'oligocène d'Europe ; relations du genre et considérations sur l'origine des ruminants.Jean SudreKeywords: Archaic Ruminants; Paleobiogeography; Quercy Phosphorites; Systematics; TragulidsAbstract The genus Cryptomeryx SCHLOSSER, 1886, inusited during a long period, has been discovered in Lower and Middle Oligocene localities of the Quercy region (South-West France). This new material, as well as specimens from the old collections referred to Cryptomeryx, are described; their study, allows us precising the definition of the genus, and confirming its allocation to the Tragulidae family. The type species of the genus, Crypmmeryx gaudryi (= Lophiomeryx gaudryi FILHOL, 1877), occurs in several localities at the base of the Middle Oligocene (Itardies, La Plante 2, Roqueprune 2, Soulce, Herrlingen 1). The new species C. matsoui n. sp. has been defined in the older locality of Mas de Got (top of Lower Oligocene). It is possible that the species Pseudamphimeryx decedens STEHLIN, 1910 pertains to the same genus. Also to the Tragulids must be referred the monospecific genus Iberomeryx (I. parvus GABOUNIA, 1964) from Upper Oligocene of Benara (Georgie, URSS), with which Cryptomeryx is related. These genera are not direct ancestors of Miocene tragulids; their occurrence in the Western European Oligocene results from a first immigration wawe of the family. These Tragulids are one of the most archaic groups of Ruminants. They are probably derived from a primitive stock which had acquired in Asia the selenodont condition of the dentition. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Fasc. 1 (1984) |
|
|

|
Nouvelle quantification de l'Hypsodontie chez les Theridomyidae : l'exemple de Theridomys ludensis nov. sp.Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Dental morphology; evolution; Hypsodonty; Oligocene; TheridomyidaeAbstract A new example of parallelism in the dental pattern ofthe Theridomyidae is illustrated by the description ofa new species: Theridomys Iudensis from the standard level of Antoingt (middle Oligocene). Considering the occurence ofthis parallelism phenomenon. the use of numerous qualitative and quantitative criteria is essential to characterize the different stages ofthe different evolutive lineages. Thus, a new simple parameter is proposed (CHY = H+l/0,5 L) to estimate hypsodonty of the medium hypsodont Rodentia. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 3 (1985) |
|
|

|
La palichnofaune de vertébrés tétrapodes du permien supérieur du Bassin de Lodève (Languedoc-France).Georges Gand, Jacques Garric, Georges Demathieu and Paul EllenbergerKeywords: Footprints; France; Languedoc; Lodève basin; new ichnotypus; Saxonian; Upper PermianAbstract Near "la Lieude", in the Lodève basin, more than a thousand of footprints are distributed in a twenty of trackways which amounts to 220 m length. They have been found on calcareous siltstone level in the B site named also "Réserve Naturelle Volontaire". This last is located in the Saxonian summit dated Upper Permian. "La Lieude" tracks are described by using statistical methods then they are compared with others from the world Permian. What allows to distinguish 4 following ichnotaxa: Lunaepes ollierorum nov.ichnosp., Merifontichnus thalerius nov. ichnogen. and nov. ichnosp., Planipes brachydactylus nov.ichnosp. and Brontopus circagiganteus nov. ichnosp. All these traces are attributed with possibility or probability to Therapsida or to Therosauria, except Brontopus circagiganteus nov. ichnosp. that could be due to Caseamorpha. All these animals whose sizes have been estimated between l and 5 m lived probably in a playa environment.The biological and sedimentological data from "la Lieude" footprints levels compared with informations provided by the tracks orientations, suggest the following scenario. Animals coming from the North have crossed a sandy channel bank with plants zones by directing to the South for the majority. Maybe, they were going to the lacustrine part of the playa, close to "la Lieude" footprints that they have just trampled on. Article infos Published in Vol. 29, Fasc. 1 (2000) |
|
|
|
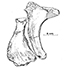
Premier signalement du Monachinae (Phocidae, Mammalia) dans le Sahélien (Miocène supérieur) d'Oran (Algérie)Christian de MuizonKeywords: Algeria; Late Miocene; PhocidaeAbstract Messiphoca mauretanica nov. gen., nov. sp. représente le premier Phocidae fossile recensé en Afrique du Nord. Provenant du gisement sahélien (Miocène supérieur) de Raz-el-Aïn (Algérie), il est connu par quelques os du membre antérieur (humérus, radius, ulna), quelques vertèbres dorsales et un crâne très fragmentaire. La description de cette forme nouvelle amène à considérer Messiphoca mauretanica comme un Monachinae archaïque proche de l'origine du groupe Pliophoca - Monachus. L'incidence de cette interprétation d'un Phocidae «pré-Messinien ›› sur la crise de salinité du Messinien est aussi envisagée. Article infos Published in Vol. 11, Fasc. 5 (1981) |
|
|
|
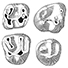
Rongeurs du Miocène inférieur et moyen en Languedoc. Leur apport pour les correlations Marin-Continental et la Stratigraphie.Jean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Languedoc; Miocene; Rodents; Southern FranceAbstract The rodents (Cricetidae, Gliridae, Sciuridae) found in lacustrine, brackish marine and karstic sediments of Miocene age in Languedoc, assign the position of the different localities in the scale of "niveaux repères" used by mammalogists. Some detailed stratigraphical studies bring several correlations between this continental biochronological scale and the marine scale ; the most important results are the Aquitanian age of the "niveaux repères" of Coderet and Paulhiac, the Burdigalian age of Laugnac, Estrepouy, Vieux-Collonges, La Romieu and Sansan and the Langhian or Lower Serravallian age of La Grive M. The correlations between the Tethys and the Central Paratethys for the Lower Neogene profit also of these results, since the locality of Neudorf Spalte 1, 2 (Czechoslovakia) is shown to be younger than Sansan (France). The paleontological study has also several geological inferences for the Miocene of Languedoc ; with the calibration of this Miocene, we know quite precisely that the Lower Miocene is chiefly a time lacustrine sedimentation, and also that the marine Miocene sedimentation ends early in the Miocene Period, in Langhian or lower Serravallian times. Article infos Published in Vol. 09, Fasc. 6 (1980) |
|
|
|
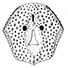
Norselaspis glacialis n.g., n.sp, et les relations phylogénétiques entre les kiaeraspidiens (Osteostraci) du dévonien inférieur du Spitsberg.Philippe JanvierKeywords: Devonian; kiaeraspids; Osteostraci; SpitsbergenAbstract The anatomy of Norselaspis glacialis n.g., n.sp., a primitive kiaeraspidian from the Lower Devonian of Spitsbergen, is described on the basis of spécimens studied by grinding sections or prepared with dilute formic acid. This study yielded some new anatomical details, including the presence of a canal prolonging posteromedially the canal alloted to the facial nerve by Stensiö. This posterior prolongation of the « facial canal ›› into the posterolateral part of the labyrinth cavity is consistent with the hypothesis put forward by Allis, Lindström, Jefferies and Whiting, that this canal housed the glossopharyngeus nerve. Furthermore, in N. glacialis, the foramen usually referred to as the foramen for the œsophagus opens posteriorly into a cavity in the postbranchial wall, referred to here as the intramural cavity, and which is interpreted as having housed the heart. Consequently, the œsophagus probably accompanied the dorsal aorta through the aortic canal. Finally, the foramen generally interpreted as having transmitted the ventral afferent arterial trunk is here considered as having housed the hepatic vein, which emptied into the venous sinus of the heart. The ventral afferent arterial trunk may thus have passed through the former «œsophageal ›› foramen. Article infos Published in Vol. 11, Fasc. 2-3 (1981) |
|
|
|
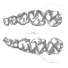
Un crane de Chalicothere (Mammalia, Perissodactyla) du Miocène supérieur de Macédoine (Grèce) : remarque sur la phylogénie des ChalicotheiinaeLouis de Bonis, Geneviève Bouvrain, George D. Koufos and Pascal TassyKeywords: Chalicotheriidae; Cladistics; Greece; Miocene; Perissodactyla; PHYLOGENYAbstract The discovery in the Turolian (Late Miocene) of Dytiko 3 (Macedonia, Greece) of a complete skull with mandibles and cervical vertebrae, atlas and epistropheus, is a very important contribution to the knowledge of the subfarnily Chalicotheríinae. After the description, the comparison with other specimens of Miocene chalicotheres permits the revival of the generic name Macrotherium with a new species M. macedonicum. This genus is mainly characterized by a short snout and an inflated cerebral skull. It coexists during the Miocene with Chalicotherium. A cladistic analysis leads to conclusion that the species which has been described from the Early Middle Miocene of Rusinga must be identified as the type-species of a new genus: Butleria. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|