Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 7- Didelphides (Marsupiaux)Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The family Didelphidae is represented by three species in the Sainte-Néboule site, phosphorites of Quercy (lower Oligocene, San Cugat's nivel): Amphiperatherium minutum (Aymard), Amphiperatherium sp. and Peratherium cuvieri (Fischer). Only the first and third species are abundant (88 and 97 pieces). This two populations are described. The marsupial fauna of the european lower Oligocene is not recognized in its entirety in this site. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
Deux nouveaux primates dans l'Oligocène inférieur de Taqah (Sultanat d'Oman): premiers Adapiformes (?Anchomomyini) de la péninsule arabique?Emmanuel Gheerbrant, Herbert Thomas, Jack . Roger, Sevket Sen and Zaher Al-SulaimaniKeywords: Adapids; Afro-Arabian plate; Early Oligocene; New taxa; Primates; Trans-Tethyan dispersalsAbstract Two new species, Omanodon minor n. g., n. sp. and Shizarodon dhofarensis n. g., n. sp., known from fifteen isolated teeth, are described here as the first adapiform primates (?Anchomomyini) recognizable to date in the Taqah material (early Oligocene of Sultanate of Oman). Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 4 (1993) |
|
|
|
Decouverte d'un nouveau Diacodexis (Artiocactyla, Mammalia) dans l'Eocène inférieur de Silveirinha, Portugal.Carmen Estravis and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Artiodactyla; Eocene; Migration; Portugal; SilveirinhaAbstract A new artiodactyl, Diacodexis antunesi n.sp., is described from the early Eocene of Silveirinha, Portugal. Comparisons are made with Diacodexis gazini GODINOT, 1978, D. varleti SUDRE et al., 1983, D. cf. varleti from Paris Basin sites, D. sp. from Dormaal and from localities in Spain and England, D. secans from North America and D. pakistanensis from Asia; affinities and evolutive tendencies are discussed. The presence of Diacodexis in the locality of Silveirinha confirms the very early Eocene age of the latter. As Diacodexis antunesi appears ta be more primitive than D. gazini from Rians (early Eocene of France), it lends corroboration to the interpretation (essentially based previously on condylarths) of the Silveirinha assemblage as the oldest Eocene fauna known in Europe and supports the hypothesis that early artiodactyls migrated from Europe to North America. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 1 (1989) |
|
|
|
L'occlusion dentaire chez Peradectes, Amphiperatherium et Peratherium, Marsupiaux du tertiaire d'Europe.Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Didelphidae; Eocene; Mastication; Oligocene; Wear facetsAbstract The general principles guiding the study of wear facets which develop during mastication in mammals possessing tribosphenic molars are named. The application of this method of study to the molars of European Tertiary Didelphidae shows that the lineage of this family as represented by the species Peratherium cuvieri (Upper Eocene), P. elegans (Lower-middle Oligocene) and P. antiquum (Upper Oligocene) has propessively evolved toward a more carnivorous diet. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
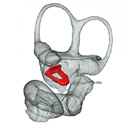
Fallen in a dead ear: intralabyrinthine preservation of stapes in fossil artiodactylsMaeva J. Orliac and Guillaume BilletKeywords: allometry; bony labyrinth; inner ear; middle ear ossiclesdoi: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e3 Abstract The stapes is the last of the middle ear ossicle chain and the smallest bone of the mammalian skeleton. Because it rests on the membrane of the fenestra vestibuli during life, the stapes may often fall within the bony labyrinth cavity when soft structures decay after death. In this work, we highlight the unexpected role that the bony labyrinth plays in the preservation of the stapes. Systematic investigation of the bony labyrinth of 50 petrosal bones of extinct and extant artiodactyls led to the discovery of eight cases of “intralabyrinthine” stapes. Three dimensional reconstructions of these stapes allow documenting stapes morphology of four extinct artiodactyl taxa: Microstonyx erymanthius (Suidae), Elomeryx borbonicus (Hippopotamoidea), ?Helohyus plicodon (Helohyidae), and an undetermined Cainotheriidae; and four extant ones Choeropsis and Hippopotamus (Hippopotamidae), and Tayassu and Phacochoerus (Suoidea). ?Helohyus plicodon from the Middle Eocene documents the oldest stapes known for the order Artiodactyla. Morphological study and metric analyses of our sample of artiodactylan stapes show that stapes are likely to carry relevant phylogenetic characters/signal within artiodactyls, and a potential Euungulata signature. Article infos Published in Vol.40-1 (2016) |
|
S.I. Data |

|
Owls, caves and fossils. Predation, preservation and accumulation of small mammal bones in caves, with an analysis of the Pleistocene cave faunas from Westbury-Sub-Mendip, Somerset, UK, par Peter Andrews, 1990. The University of Chicago Press, 232 p.Christiane DenysKeywords: caves; owls; preservation; taphonomyAbstract La taphonomie (science de l'enfouissement et de la fossilisation) des micromammifères a trop souvent été négligée par rapport à celle des grands mammifères. Or, pour expliquer les concentrations parfois très importantes de microfossiles dans les grottes et les sites préhistoriques il faut connaître les mécanismes qui concourrent actuellement à favoriser les accumulations de ces derniers. C'est le but de l'ouvrage de Peter Andrews qui se décompose en deux parties. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 1 (1992) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude des micromammifères du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). 1- Le gisementJean-Pierre Aguilar and Jean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Hérault; Late Miocene; Micromammals; MontredonAbstract La localité fossilifère du Puech de Montredon, désignée plus communément sous le nom de Montredon, est située sur la commune de Montouliers (Hérault) à quelques 300 mètres de la limite avec le département de l'Aude. Elle a été découverte en 1845 par Narbonne, Directeur des Mines de La Caunette, et de très nombreux restes de vertébrés continentaux y ont été extraits. La plus ancienne mention de ce gisement dans la littérature semble être celle de Lartet (1859) qui signale que "M. Jourdan, de Lyon, a constaté à Montredon, près de Bize (Aude), l'association des restes de Dinotherium avec l'Hipparion". Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 3 (1982) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude des micromammifères du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). 4 - Les chiroptèresBernard SigéKeywords: Chiroptera; Hérault; Late Miocene; Micromammals; MontredonAbstract The Montredon local fauna yielded very rare bats, represented by damaged isolated teeth. Only a few documents are available for this period of the European Neogene. ln this poor state of knowledge, the material represents three undetermined species, a supposed molossid and two vespertilionids. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 3 (1982) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 7 - Les proboscidiens DeinotheriidaeHeinz TobienKeywords: allometry; Astaracian; Deinotherium; Montredon; Systematics; taphonomy; VallesianAbstract Some complete tooth rows and about one hundred isolated teeth enabled the identification of the deinothere of the Vallesian site Montredon (Hérault) as Deinotherium giganteum KAUP 1829, mainly by comparisons with the likewise Vallesian sample of the type locality Eppelsheim (Rheinhessen, F.R.G.). Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
Latest Early-early Middle Eocene deposits of Algeria (Glib Zegdou, HGL50), yield the richest and most diverse fauna of amphibians and squamate reptiles from the Palaeogene of AfricaJean-Claude Rage, Mohamed Adaci, Mustapha Bensalah, Mahammed Mahboubi, Laurent Marivaux, Fateh Mebrouk and Rodolphe TabuceKeywords: Africa; Algeria; amphibians; Eocene; squamatesdoi: 10.18563/pv.44.1.e1 Abstract HGL50 is a latest Early-early Middle Eocene vertebrate-bearing locality located in Western Algeria. It has produced the richest and most diverse fauna of amphibians and squamate reptiles reported from the Palaeogene of Africa. Moreover, it is one of the rare faunas including amphibians and squamates known from the period of isolation of Africa. The assemblage comprises 17 to 20 taxa (one gymnophionan, one probable caudate, three to six anurans, seven ‘lizards’, and five snakes). Two new taxa were recovered: the anuran Rocekophryne ornata gen. et sp. nov. and the snake Afrotortrix draaensis gen. et sp. nov. The locality has also yielded the first confirmed anilioid snake, the first Palaeogene gymnophionan, and probably the first caudate from the Palaeogene (and possibly from the Tertiary) of Africa. The presence of a caudate at that time in Africa would be of particular interest; unfortunately, the available material does not permit a definitive identification. The fauna comprises Gondwanan and more specifically West Gondwanan vicariants, probably autochthonous groups and a Eurasian immigrant (assuming that the identification of the caudate is accurate). The fauna from HGL50 is clearly distinguished from the few other Eocene assemblages of Africa. However, if this results largely from differences in geological ages, geographic positions of the localities and mainly differences in environments took a part in the composition of the faunas. Article infos Published in 44-1 (2021) |
|
|
|
Etude de la Variabilité chez Lophiodon lautricense NouletJean SudreKeywords: Cheek teeth; Eocene; Lophiodon; variabilitydoi: 10.18563/pv.4.3.67-95 Abstract The biometric and morphologie variability of the cheek teeth in the end-of-the-phylum species Lophiodon lautricense Noulet studied in this note, reposes on the observation of about 800 teeth. These were revealed to be little variable in absolute dimensions. The considerable morphologie variability in the upper premolars permitted the problem of the molarization process to be taken up. An hypothesis concerning the order of eruption of the cheek teeth is formulated based on an examination of a large number of milk dentitions. In conclusion, it is suggested that reservations be held on the value of dental characters classically used in systematics for the group under consideration. Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 3 (1971) |
|
|
|
Leptacodon nascimentoi n,sp., un nouveau Nyctitheriidae (Mammalia,Lipotyphla) de l'Eocène inférieur de Silveirinha (Baixo Mondego, Portugal)Carmen EstravisKeywords: Eocene; Leptacodon; Lipotyphla; Mammals; Nyctitheriidae; Portugal; SilveirinhaAbstract In this article is described a new species of Nyctitheriidae with primitive characters: Leptacodon nascimentoi n. sp. from the early Eocene of Silveirinha (Portugal). Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 3 - Les artiodactyles ruminantsLéonard Ginsburg and Herbert ThomasKeywords: Artiodactyla; France; Montredon; Ruminentia; Upper MioceneAbstract The remains of Ruminantia are very rare at Montredon. No specific determination was possible. We have only one Micromeryx, one small cervid, one tragocere and one (?) gazella. The faunal spectrum is in good correlation with the general retreat of the cervids in the European upper Miocene, but in contrast it is not convenient for the bovids, which are in expansion at the same time. For them, we have to invoke the local ecological conditions. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
Avant propos au "Premier catalogue des specimens-types Paléontologiques déposés dans les collections de l'Université de Montpellier II"Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Editorial; Type specimensAbstract Avant propos au "Premier catalogue des specimens-types Paléontologiques déposés dans les collections de l'Université de Montpellier II". View editorial Published in Vol. 23, Ext (1994) |
|
|

|
Rongeurs caviomorphes de l'Oligocène de Bolivie. 1 Introduction au deseadien de BolivieRobert HoffstetterKeywords: Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract The Tertiary of the Salla-Luribay basin consists of red beds affected by the second period of the andine compression, of Miocene ending age. The Tertiary layers are exposed at an approximate elevation of 3.500 to 4.000 meters. Two stratigraphic units can be distinguished in them: the Luribay conglomerates, in which vertical clifts result from erosion, and the Salla layers consisting mostly of consolidated clays. These clays are very fossiliferous and have furnished a rich vertebrate fauna which gave to R. Hoffstetter the possibility to establish the Oligocene age of these beds. Sediments of same age has been reported to be present in several other places of Bolivia, particularly near Lacayani, where have been collected highly hypsodont Rodents, different from those found in Salla-Luribay basin. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 3 (1976) |
|
|
|
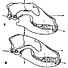
Les Affinités de Nyctereutes megamastoides (Pomel), canidé du gisement Villafranchien de Saint-Vallier (Drôme, France).R. MartinKeywords: Canidae; Nyctereutes; Villafranchiandoi: 10.18563/pv.4.2.39-58 Abstract Nyctereutes megamastoides (Pomel) from the Villafranchian of the Auvergne and from Saint-Vallier presents cranial and dental characters sufficiently close to those of the late Pliocene canid from Perpignan (Roussillon), described by Depéret under the specific name of Canis donnezani belonging to the same genus Nyctereutes. The extinction of the European "Nyctereutes" group seems due to the too great alimentary specialization of this canid, whereas the Asiatic lineage represented in the Villafranchian by Nyctereutes sinensis Schlosser and at present by Nyctereutes procyonider Gray was able to maintain itself probably by means of a profound change in its alimentary regime. Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 2 (1971) |
|
|

|
Pseudorhyncocyon cayluxi Filhol, 1892 insectivore géant des phosphorites du QuercyBernard SigéKeywords: Insectivores; Leptictidae; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Une hémimandibule et une molaire supérieure recueillies dans le gisement oligocène inférieur d'Escamps (phosphorites du Quercy) fournissent de nouvelles informations sur le genre Pseudorhyncocyon FllHOL, grand insectivore longirostre du Paléogène d'Europe, fossile très mal connu jusqu'ici. Des comparaisons avec les macroscélididés africains, géolabididés nord-américains, et leptictidés euraméricains permettent de rattacher cet amimal aux leptictidés, et de le rapprocher du genre Lepticidium TOBIEN, au sein de la sous-famille européenne nouvelle des pseudorhyncocyoninés. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 12- Fissipèdes (Carnivores)Louis de BonisKeywords: Carnivora; Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Les Carnivores Fissipèdes de Sainte-Néboule appartiennent tous au genre Cynodictis et semblent constituer une population homogène. Celle-ci se distingue suffisamment des espèces déjà décrites pour constituer un taxon particulier : Cynodictis lacustris neboulensis n. s. sp. . L'étude des variations à l'intérieur de cette population nous a conduit à reconsidérer les critères utilisés pour définir les espèces existantes et à regrouper certaines d'entre elles. Il semble qu'il demeure cependant trois lignées distinctes dans le genre Cynodictis mais le matériel nous paraît encore insuffisant pour traduire cette remarque en termes de systématique. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Morphotypes dentaires actuels et fossiles des Chiroptères Vespertilioninés. 1e partie: Etude des morphologies dentairesHenri MenuKeywords: bats; Dental morphology; fossils; PHYLOGENY; recent; SystematicsAbstract The classifications of the recent vespertilionine bats were made wihtout taking in account the teeth morphology; this resulted in a reduction of the possibilities of comparison with the available fossils. The generalized use of dental formulae was abusive: this contributed to the admission of artificial genera. These conditions have long delayed the consideration of characters able to frame the phylogeny of the sub-family. In the first part of the study, the teeth morphologies are described and analysed. morphological reference types are established for each upper and lower tooth: they should make an easier elaboration of criteria for the differentiation at generic level. The position of the species in view of these criteria allows one to group them into homogeneous genera, and to appreciate the degree of relationship that the latter have between them. The second part of the study (next publicationà will develop inferences dealing with systematics and phylogeny Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 2 (1985) |
|
|

|
Origins of avian reproduction: answers and questionsfrom dinosaurs.David J. Varricchio and Frankie D. JacksonKeywords: Avian reproduction; clutch; dinosaurs; egg size; nests; oviducts; parental careAbstract The reproductive biology of living birds differs dramatically from that of other extant vertebrates. Distinctive features common to most birds include a single ovary and oviduct, production of one egg at daily or greater intervals, incubation by brooding and extensive parental care. The prevalence of male parental care is most exceptional among living amniotes. A variety of hypotheses exist to explain the origin of avian reproduction. Central to these models are proposed transitions from a condition of no care to maternal, paternal or biparental care systems. These evolutionary models incorporate a number of features potentially preservable or inferable from the fossil record (integument, skeletal adaptations for flight, egg and clutch size, nest form, hatchling developmental stage, the number and function of oviducts, and the mode of egg incubation). Increasing availability of data on dinosaur reproduction provides a means of assessing these hypotheses with fossil evidence. We compare dinosaur data to a selection of models that emphasize maternal, paternal or biparental care. Despite some congruence with dinosaur features, no single model on the evolution of avian reproduction conforms fully to the fossil record, and the ancestral parental care system of birds remains ambiguous. Further investigation into dinosaur parental care, nest structures, clutch geometry, egg-pairing, eggshell porosity, and embryo identification may eventually resolve these issues. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|