Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Rodent paleocommunities from Ulantatal
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
|
|
|
|
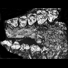
Un Haplobunodontidae nouveau Hallebune krumbegeli nov.gen. nov.sp. (Artiodactyla, Mammalia) dans l'Eocène moyen du Geiseltal près Halle (Sachsen-Anhalt, Allemagne)Jorg Erfurt and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyla; Geiseltal; Germany; Mammal; Middle Eocene; new gen.; new sp.Abstract A new genus and species of haplobunodontid artiodactyl, Hallebune krumbiegeli nov. gen. nov. sp., is described from the middle Eocene Geiseltal Fauna (Saxon-Anhalt, Germany). Its stratigraphic range is restricted to the MP 13 ("obere Mittelkohle") of the Geiseltalian. The material consists of seven fragments, representing both upper and lower jaws. It is indicated, that H. krumbiegeli was a small bunodont herbivore. The size and primitive character of the teeth suggest that the genus possibly is directly derived from Diacodexeidae.The new material forms the basis for reinterpreting the haplobunodontid phylogeny. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 1-2 (1995) |
|
|

|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. Avant propos.Bernard SigéKeywords: Editorial; Mammalia; Montredon; Upper MioceneAbstract Le Mémoire Extraordinaire 1988 de PALAEOVERTEBRATA regroupe dix articles consacrés au gisement à mammifères du Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault), connu et classique depuis la fin du siècle dernier, et auquel est lié le nom du savant paléontologue lyonnais Charles Depéret. View editorial Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
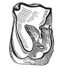
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 3 - Les artiodactyles ruminantsLéonard Ginsburg and Herbert ThomasKeywords: Artiodactyla; France; Montredon; Ruminentia; Upper MioceneAbstract The remains of Ruminantia are very rare at Montredon. No specific determination was possible. We have only one Micromeryx, one small cervid, one tragocere and one (?) gazella. The faunal spectrum is in good correlation with the general retreat of the cervids in the European upper Miocene, but in contrast it is not convenient for the bovids, which are in expansion at the same time. For them, we have to invoke the local ecological conditions. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
Hyracodontids and rhinocerotids (Mammalia, Perissodactyla, Rhinocerotoidea) from the Paleogene of MongoliaDemberelyin DashzevegKeywords: Hyracodontidae; Mongolia; Paléogène; Perissodactyla; RhinocerotidaeAbstract Two families are reviewed (Hyracodontidae and Rhinocerotidae) from the Paleogene of Mongolia. The following taxa are described from the former family: Triplopus? mergenensis sp. nov., Prohyracodon meridionale CHOW, Prohyracodon? parvus sp. nov., Forstercooperia ergiliinensis GABUNIA & DASHZEVEG, Ardynia praecox MATTHEW & GRANGER, A. mongoliensis (BELIAYEVA), Ardynia sp., Urtinotheríum sp. (or Indricotherium) and Armania asiana GABUNIA & DASHZEVEG. All of them are from the Paleogene of the eastem Gobi Desert The hyracodontid Pataecops parvus RADINSKY is described from a new locality, Menkhen-Teg (Middle Eocene), in the Valley of Lakes. Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Fasc. 1-2 (1991) |
|
|

|
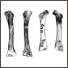
Contributions à l'étude des micromammifères du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). 2- Les rongeursJean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Hérault; Late Miocene; Micromammals; Montredon; RodentsAbstract The recent excavation of the Upper Miocene locality of Montredon (Hérault) provides a rich material of Mammals. The present study deals with rodents. The new quarry is 10 meters above the classical Depéret's Quarry. No differences have been noticed between the rodent populations coming grom these two sites. The description of two new species : Hispanomys mediterraneus and Muscardinus heintzi is given and the dormouse Eliomys is recorded there for the first time. The new zonation of the Miocene given by Aguilar (1982) and the previously established correlations between marine and continental chronological scales give Tortonien age (estimated between 9 and 10 M.Y. old) to the site of Montredon, which belongs to the Mammal zone D 2. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 3 (1982) |
|
|
|
La poche à Phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 6- OiseauxCécile Mourer-ChauviréKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract There are very few birds in the site of Sainte-Néboule. They belong to three species already known in the "Phosphorites" : Paraortyx brancoi, Aegialornis broweri, Cypselavus gallicus, and to one new species, Recurvirostra santaeneboulae. The comparison of some different bones of the genus Cypselavus with some Apodiformes and Caprimulgiformes shows that this genus must be classified in the order Apodiformes. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
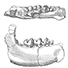
Etude des dents jugales inférieures des Equus (Mammalia, Perissodactyla) actuels et fossilesVéra EisenmannKeywords: Cheek teeth; Equus; MammalsAbstract The comparative morphology and biometry of the lower cheek teeth of modern Equus are studied on approximately 300 mandibles belonging to the 10 usually recognised species : Equus grevyi, E. burchelli, E. quagga, E. zebra, E. africanus, E. asinus, E. hemionus, E. klang, E. przewalskii, E. caballus. The studied parameters comprise : occlusal length and width, postflexid length and index ; shape of the double knot (metaconid + metastylid + lingual groove) ; depth of the vestibular groove on the molars ; frequency of the pli caballinid, protostylid and other enamel plications or islets ; frequency of the dP/l. Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 3-4 (1981) |
|
|
|
Les mammifères de Rians (Eocène inférieur, Provence)Marc GodinotKeywords: Eocene; Mammals; Provence; RiansAbstract The fossil mammals discovered in the quarry of Rians (Sparnacian, Provence) are described. Among these forms, Hyracotherium is interesting because of the little molarization of the lower premolars and its small size, and Diacodexis by its small size and very primitive astragalus ; they may be the most primitive representatives of their respective orders. Also, Proviverra eisenmanni n. sp. is the smallest and most primitive hyaenodontid yet described. Hyopsodus itinerans is the first species of this genus described France. Among other rare fossils is a new species of bat, a small palaeoryctid, and other forms not yet identified. Marsupials are varied. Several new species are present among the rodents. The fauna is well-balanced and rich in small hyopsodontid condylarths. It is stratigraphically situated at the Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 2 (1981) |
|
|

|
Sur le remplissage des "poches à phosphorite" d'Aubrelong (commune de Bach, Lot)Bernard GèzeKeywords: Aubrelong; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|
|
Ostéologie de la tête de Richardus excavans Lavocat,1988René LavocatKeywords: Africa; anatomy; Bathyergidae; Miocene; RodentsAbstract Remarkable association of a small infraorbital foramen, similar to that in recent Heterocephalus, and of a strong muscular print on the dorsal anterior part of the zygomatic plate and on the premaxillary. Several anatomical structures to be compared with those of Heterocephalus suggest relationships with this genus. Richardus supports the ancestrality of the hystricomorph character in the bathyergids Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 2 (1989) |
|
|
|
Prospection paléontologique de la région de Torralba de Ribota (Burdigalien du bassin de Calatayud, prov. de Zaragoza, Espagne)Edouard Boné, Maria T. Alberdi, Manuel Hoyos and Nieves Lopez-MartinezKeywords: Faunal assemblage; Macromammals; Spain; Zaragoza prov.Abstract The study of another faunal assemblage (mostly macromammals) from Torralba de Ribota (Calatayud, Zara- Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
La poche à Phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertébres du Ludien supérieur. 5-SquamatesJean-Claude RageKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The Squamates from Sainte-Néboule are charateristic of the Upper Eocene from the Phosphorites du Quercy. Most genera known from this locality do not survive the « Grande Coupure ». Cadurcoboa insolita gen. nov., sp. nov. is a small Boidae very characteristic of the Upper Eocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|

|
Le genre Mesembriacerus (Bovidae, Artiodactyla, Mammalia) : un Oviboviné primitif du Vallésien (Miocène supérieur) de Macédoine (Grèce)Geneviève Bouvrain and Louis de BonisKeywords: Bovidae; Cladistics; Late Miocene; Ovibovinae; VallesianAbstract The bovid Mesembriacerus melentisi, the numerous skulls, teeth and limb bones of which are described from the locality Ravin de la Pluie (Macedonia, Greece), bears some features which allow us to put it in the tribe ovibovini (Ovibovinae) with several other Miocene genera and the Recent one Ovibos. A cladogram gives the phyletic relationships within this tribe. It shows that Mesembriacerus which is one of the oldest genera, is also the most primitive. The limb bones are as elongated as those of Recent cursorial bovids and they show, as does the bulk of the fauna, an open environment for the locality. Article infos Published in Vol. 14, Fasc. 4 (1984) |
|
|

|
Les mammifères Montiens de Hainin (Paléocène moyen de Belgique) Part II : Les CondylarthresJean Sudre and Donald E. RussellKeywords: Belgium; Condylarths; Louisininae; Oxyclaeninae; PaleoceneAbstract The Condylarths from Hainin (Hainault, Belgium) show no affinity at the generic level to those known in other Paleocene localities of Europe and North America ; they are described as new forms : Monshyus praevius n. gen., n. sp. and Prolatidens waudruae n. gen., n. sp. Monshyus praevius, discovered in only one of the levels in the excavation at Hainin, is similar to the genera Microhyus TEILHARD and Louisina RUSSELL ; with them it is included in the subfamily Louisininae (Hyopsodontidae). With respect to Microhyus and Louisina, Monshyus is distinguished by the precociously modern aspect of its upper molars, the only teeth that are referable. Prolatidens waudruae, known only by lower molars, was found in several levels in the pit at Hainin. It is an arctocyonid presenting possible relationships to the North American form Oxyprimus galadrielae ; it therefore has been provisionally attributed to the subfamily Oxyclaeninae. If this attribution is confirmed, this species will constitute the first and only representative of the group in Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 6 (1982) |
|
|
|
Nouveaux gisements à rongeurs dans les molasses oligo-miocènes de la région toulousaineFrancis DuranthonKeywords: Cricetidae; Eomyidae; GIiridae; Miocene; Oligocene; Rodents; Sciuridae; Southern FranceAbstract The fauna from three new rodent localities (Castelmaurou, Grépiac-carrière et Grépiac-rive gauche) from Oligo-Miocene molasses of the Toulouse area is described. The one from Colomiers is completed. 11 species belonging to 4 families (Cricetidae, Eomyidae, Gliridae, Sciuridae) are present. The Miocene localities of Grépiac-carrière and Colomiers are correlated with Balizac, La Brète, Lambert and Lespignan. Grépiac-rive gauche is just a little older than these sites. Castelmaurou is somewhat younger than La Milloque and belongs to Oligocene. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|
|
Les rongeurs de l'Oligocène inférieur d'EscampsMonique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Escamps; Quercy Phosphorites; Rodents; TheridomyidaeAbstract La faune de Rongeurs d'Escamps (Lot) bien que relativement pauvre en espèces (dix) s'avère riche d'enseignement pour les Rongeurs de l'Oligocène inférieur d'Europe Occidentale. Cette periode semble caracterisée par une cladogenèse des Théridomyines. A Escamps, un nouveau genre (Patriotheridomys) est décrit ainsi qu'une nouvelle espèce de Theridomys. Avec Oltmamys platyceps, décrit ici plus complètement et désormais bien situé stratigraphiquement, les deux espèces précédentes constituent un ensemble original du Sud de la France. A la même époque, en Angleterre, Allemagne et Espagne, des espèces «régionales» de Théridomyinés se dersifient. A côté de ces formes qui ne semblent pas franchir la «Grande Coupure» sont représentées deux lignées d'Issiodoromyinés (Elfomys sp et Pseudoltmomys cuvieri), une de Théridomyiné (T. (Blainvillimys) rotundidens) ainsi qu'un Gliridé, Gliravus priscus (que l'on différencie nettement de la deuxième lignée des Gliravus oligocènes : G. meridionalis -> G. majori). On retrouve ces formes dans les gisements plus récents du niveau de Hoogbutsel où elles sont à peine plus évoluées. Le fait que les degrés évolutifs de ces lignées soient très proches laisse supposer que le laps de temps séparant les niveaux d'Ecamps et Hoogbutsel fut relativement court. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 3-4 (1975) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 4 - Les artiodactyles Suidae.Léonard GinsburgKeywords: Artiodactyla; France; Mammalia; Montredon; Upper MioceneAbstract There is only one suid known in the Upper Miocene of Montredon (Hérault): Microstonyx (Limnostonyx nov. subgen.) antiquus (KAUP). It is differenciated from Microstonyx major by the presence of upper and lower canines which are considerably longer and biger. Its presence at Montredon corroborates the palustrine habitat for the species. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
Les rongeurs de l'Eocène d'Afrique Nord-Occidentale [Glib Zegdou ( Algérie) et Chambi (Tunisie)] et l'origine des anomaluridae.Monique Vianey-Liaud, Jean-Jacques Jaeger, Jean-Louis Hartenberger and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Africa; Eocene; New taxa; Paleobiogeography; PHYLOGENY; RodentsAbstract This paper is about the oldest African rodents faunas, from the late Early Eocene, or early Middle Eocene, Glib Zegdou (Algeria) and Chambi (Tunisia) localities. Five species are described and figured, belonging to a new family here created, the Zegdoumyidae. Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|

|
Die Referenzfauna des Geiseltalium, MP levels 11 bis 13 (Mitteleozan, Lutetium)Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Eocene; Geiseltal; Land mammal ages; Mammalian reference levelsAbstract The Middle Eocene Fossillägerstätte of the Geiseltal lignite beds near Halle/S. (German Democratic Republic) is the reference locality of the European land mammal age Geiseltalian and of the Mammalian Paleogene reference levels MP 11 - MP 13. Due to this importance a reinvestigation is given of the lithostratigraphical development of the Geiseltal beds and of their vertebrate sites. The last are genetically related to the southwest border of the Geiseltal depression and the influx of carbonate-rich waters. The geographical distribution and stratigraphical position of the fossiliferous sites depends on subrosive and tectonically controlled distribution of coal seams. The geological factors and the known stratigraphical guide of some mammalian species suggest corrections of the age of some sites. Four of the alltogether five coal bearing phases contain the 35 sites with mammalian remains. By the distribution of the around 69 mammal species are characterized, with 5 faunal steps ranging from MP 11 to MP 14 or over the Geiseltalian up to the Lower Robiacian. Well distant are the faunas of MP 11 and MP 12. Beginning with MP 12 up to MP 13/14, the fossil record is very frequent by 27 sites. This evidence coincides somewhat more with the concept of land mammal ages compared to that of the punctual mammalian reference levels. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|