Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Two enigmatic rodents from Lavergne (MP 16), Quercy Phosphorites
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
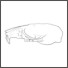
Les rongeurs du Miocène moyen et supérieur du MaghrebJean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Neogene; North Africa; RodentiaAbstract The Faunas of Rodents from seven north-african fossiliferous beds distributed from the Middle up to the Uppest Miocene are studied. One genus, seventeen species, one subspecies described are new. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 1 (1977) |
|
|
|
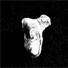
Les Ischyrictis de la transition Vindobonien-VallésienMiquel Crusafont i PairóKeywords: Ischyrictis; MustelidaeAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 5 (1972) |
|
|
|
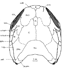
Les vertébres dévoniens de la Montagne Noire (Sud de la France) et leur apport à la phylogénie des pachyosteomorphes (Placodermes Arthrodires).Hervé Lelièvre, Raimund Feist, Daniel Goujet and Alain BlieckKeywords: Devonian; Montagne Noire; New taxon; PHYLOGENY; Placoderms; Stratigraphy; VertebrateAbstract Several different taxa of jawed vertebrates are reported for the first time from the Devonian of south-eastern Montagne Noire, France. Besides some undeterminable fragments of placoderm fishes from the Pragian and Lower Emsian, the material from the Upper Devonian is mainly represented by Melanosteus occitanus gen. and sp. nov. (Frasnian) and Thoralodus cabrieri LEHMAN, 1952 ("Famennian"). The good state of preservation of Melanosteus allows a detailed anatomical study leading to a phylogenetic analysis of the selenosteid pachyosteomorphs. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 1 (1987) |
|
|
|
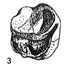
Un giraffidae dans le pliocène de Montpellier ?Claude GuérinKeywords: Artiodactyla; France; Giraffidae; Mammalia; Montpellier; RuscinianAbstract An upper giraffid premolar without any indication about its origin is preserved at the Montpellier University among numerous fossils from the ruscinian formation of Montpellier. It can be related to Samotherium, of the Upper Miocene in Eastern Europe, North Africa and Asia, or more probably to Bramatherium or Hydaspitherium of the Pliocene of South East Asia. The sedimentological study of the matrix shows a calcareous background, which may indicate that this tooth does not come from the Montpellier formation. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 3 (1986) |
|
|

|
Physogaleus hemmooriensis (Carcharhinidae, Elasmobranchii), a new shark species from the early to middle Miocene of the north sea basin.Thomas Reinecke and Kristiaan HoedemakersKeywords: Carcharhinidae; Early Miocene; Elasmobranchii; Hemmoorian; new species; North Sea Basin; PhysogaleusAbstract A new carcharhinid shark species, Physogaleus hemmooriensis sp. nov., is described from the Lower Hemmoorian (Behrendorfian, late Burdigalian, early Miocene) of Werder, Lower Saxony, Germany. P. hemmooriensis also occurs in the Edegem and Antwerpen Sands Members of the Berchem Formation, Belgium, and in the Miste Bed, Aalten Member of the Breda Formation, The Netherlands, which have an early to middle Miocene age. In the Western Atlantic region, the taxon is present in the early Miocene Calvert Formation of Delaware, U.S.A, which is largely contemporaneous with the Hemmoorian. Article infos Published in Vol. 34, Fasc. 1-2 (2006) |
|
|

|
Revision der Equoidea aus den Eozänen Braunkohlen des Geiseltales bel Halle (DDR).Jens L. Franzen and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Eocene; Europe; Mammalia; Perissodactyla; Stratigraphy; taxonomyAbstract The dentitions as well as one complete and several partial skeletons of Equoids from the Eocene lignite beds of the Geiseltal locality are revised. Instead of 13 species distinguished up to now 3 chronoclines with 5 species and 3 separate species are recognized (text. fig. 1). Propalaeotherium hassiacum HAUPT, 1925 is evolving into Propalaeotherium isselanum (CUVIER, 1824) between the levels of the « obere Unterkohle ›› and the « untere Mittelkohle ›› of the Geiseltal section. Propalaeotherium argentonicum GERVAIS, 1849 is shown to be present in the « untere Unterkohle ››, whereas Lophiotherium pygmaeum (DEPERET,1901) occurs in the « obere Mittelkohle ›› and in the « oberes Hauptmittel ››. Plagiolophus cartieri STEHLIN, 1904 appears during the transition from the « Mittelkohle ›› into the « Oberkohle ›› as the earliest true Palaeothere. Therefore the « Oberkohle ›› is already regarded as Upper Eocene. This is corroborated by the occurrence of a phyletic descendant of Propalaeatherium parvulum (Propalaeotherium n.sp.) in the middle and upper "Oberkohle " because this species appears otherwise for the first time at the mammal level of Lissieu. On the other hand Propachynolophus gaudryz (LEMOINE, 1878) described by Matthes (1977) from the « untere Unterkohle ›› turns out te be in fact a Phenacodont. Thus the decisive argument for classifying the « untere Unterkohle ›› as Lower Eocene has to be dropped. Biostratigraphically the « Unterkohle ›› and the «Basishauptrnittel ›› correspond with the lower Middle Eocene (mammal level of Messel), whereas the «unteres Hauptmittel ›› and the « untere Mittelkohle ›› are equivalent to the middle part of the middle Eocene (mammal level of lssel), and the « obere Mittelkohle ›› together with the « oberes Hauptmittel ›› coincide with the upper Middle Eocene (mammal level of Bouxwiller). Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 1 (1986) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 8 - Analyse paléoécologique de la faune mammalienneSerge LegendreKeywords: France; Mammalia; Montredon; Paleoecology; Upper MioceneAbstract The species diversity of the mammalian fauna from Montredon (Hérault, France, late Miocene) is examined in terms of richness and abundance. A cenogramic analysis of the fossil mammalian community suggests the prevalence of open habitats, with the presence of marshes and of a poorly developed galery forest, and a climate rather warm and dry. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|

|
Relations phylétiques de Bachitherium filhol, ruminant de l'Oligocène d'Europe Occidentale.Denis Geraads, Geneviève Bouvrain and Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyla; Bachitherium; Cladistic analysis; France; Mammalia; Oligocene; RuminantiaAbstract A detailed comparative study of a complete skeleton of Bachitherium and a cladistic analysis of the sub-order Neoselenodontia lead us to propose a cladogram and a new classification of this group. The Tylopoda are the sister-group of the Ruminantia, which are chiefly defined by the fusion of the cuboid and navicular. Within this infra-order, Amphimeryx is the sister genus of a tetraselenodont group, in which the Hypertragulidae are well-separated group from a monophyletic group defined by the loss of trapezium, fusion of capitatum and trapezoid, and the isolation of the hypoconid on lower molars. The most primitive genera of this group, Lophiomeryx and Iberomeryx still have an open trigonid on the lower molars, but this is lingually closed in Archaeomeryx, sister-genus of the higher Ruminantia which have fused metatarsals and more evolved milk teeth. We divide them into two pan/orders : Tragulina (including the recent and miocene Tragulidae, and the North-American Leptomerycidae), and Pecora, with reduced lateral metacarpals and a new crest (telocristid) on the lower premolars. Within the Pecora, the upper molars of Gelocus are more primitive than those of Bachitherium (a genus with many autapomorphies in the dentition) itself more primitive than the group Prodremotherium + Eupecora, with fused metacarpals. We consider the Eupecora (including several genera without frontal appendages) to be monophyletic. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 2 (1987) |
|
|

|
L'anatomie de Lyrocephaliscus euri (wiman), Trématosaure du Trias inférieur du Spitsberg : arrière-crâne, squelette axial et ceinture scapulaire.Jean-Michel Mazin and Philippe JanvierKeywords: skull anatomy; Spitsbergen; Trematosaurs; TriasAbstract The formic acid preparation of a nodule collected from the Lower Triassic of Spitsbergen, and containing a skull with some associated postcranial elements of Lyrocephaliscus euri (WIMAN), precises and enriches previous descriptions of the reputedly well-known trematosaur. lt permits more detailed descriptions of the occipital region, of the course of the carotid arteries and collateral vessels, and refutes the previous description of a stapedial foramen in trematosaurs. The discovery of pleurocentres associated with the other vertebral components confirms the primitive rhachitomy of trematosaurs. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 1-2 (1983) |
|
|
|
Schmelzmikrostruktur in den inzisiven alt-und neuweltlicher histricognather nagetiereThomas MartinKeywords: Africa; Caviomorpha; Ctenodactyloidea; Deseadan; Enamel microstructure; Hunter-Schreger bands; Hystricognathi; Incisors; Ischyromyoidea; multiserial; Paleobiogeography; pauciserial; Phiomorpha; Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract Enamel microstructure in the incisors of Old- and New World hystricognath rodents: Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Ext (1992) |
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
Ein neuer condylarthre und ein tillodontier (Mammalia) aus dem Mitteleozän des Geiseltales.Jens L. Franzen and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Condylarthra; Eocene; Europe; Mammalia; taxonomy; TillodontiaAbstract In the course of a revision of the Equoidea numerous dentitions as well as a partial skeleton of a Phenaeodont were discovered from the Middle Eocene lignite beds of the Geiseltal locality. These fossils are recognized as a new genus and species of Phenacodontidae : HaIlensia matthesi n.g. n.sp.. The species is present in the « untere und obere Unterkohle ›› (uUK, oUK = the lower and upper part of the Lower Coal Seam) as well as in the « obere Mittelkohle ›› (oMK = the upper part of the Middle Coal Seam). Two fragmentary upper jaws described and figured by Matthes (1977) as Propachynolophus gaudryi are also belonging to Hallensia matthesi. Thus the decisive argument for classifying the " Unterkohle " of the Geiseltal section as Lower Eocene has to be dropped. Another relict form of the Geiseltal is Esthonyx tardus n. sp. documented by a fragmentary mandible coming from the « untere Unterkohle ››. This is the latest Tillodont from Europe. Contrasting to E. munieri from the european Lower Eocene the dentition of E. tardus is morphologically more progressive. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 1 (1986) |
|
|

|
Une faunule de vertébrés sous la base de grès de Celas (Eocène supérieur) à ST Dresery (Gard)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Artiodactyla; Biostratigraphy; Eocene; MammalsAbstract The St-Dézéry local fauna (3 reptile-, 4 mammal species) is approximately of the same age as the La Débruge or the Ste-Néboule faunas. It conduces to a better dating of the limestones underlying the Célas sandstones. A large part of a mandible of Amphimeryx was found there, which documents the record of this family of small artiodactyls Article infos Published in Vol. 23, Fasc. 1-4 (1994) |
|
|
|
Evolution et extinction des reptiles marins au cours du Mésozoïque.Nathalie BardetKeywords: Crocodiles; evolution; Extinctions; faunal assemblages; Helveticosaurs; Hupehsuchians; Ichthyoaurs; lizards; Marine Reptiles; Mesozoic; Nothosaurs; Pachypleurosaurs; Placodonts; Plesiosaurs; Snakes; Thalattosaurs; Turnovers; TurtlesAbstract An interpretation of the marine reptile fossil record, based on the existing litterature and complemented by the review of ancient collections and the study of new material, permits a better understanding of Mesozoic marine ecosystems. An inventory of the marine reptiles known from the Lower Triassic to the Paleocene is presented: 46 families, about 200 genera and 400 species have been recorded. This data base includes commentaries about systematics, stratigraphical ranges and geographical distribution of taxa. Marine reptiles include a mosaic of not necessarily closely related groups: ichthyosaurs, thalattosaurs, hupehsuchians, pachypleurosaurs, placodonts, nothosaurs, plesiosaurs, pliosaurs but also crocodiles, lizards, snakes, turtles. The diversity studies reveal that the fossil record of marine reptiles has been punctuated by two mass extinctions, during the Middle-Upper Triassic transition and at the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary. The Jurassic-Cretaceous and Cenomanian-Turonian boundaries (the latter marked by the disappearance of ichthyosaurs) are potential crisis periods, but current data are not sufficient to reach conclusions. The Ladinian-Carnian transition is characterized by the disappearance of 64 % of families and affects essentially coastal forms. This extinction coincides with an important regressive phase. During the Upper Triassic, a faunal reorganisation within marine reptiles leads to the progressive disappearance of near-shore forms and to the development of pelagic groups. During the Maastrichtian-Danian crisis, 36% of families died out. Large-sized pelagic forms such as mosasaurs and elasmosaurs were the most affected and their extinction seems to have been rather sudden. On the other hand, pliosaurs and protostegid turtles became extinct, but were already declining. The survivors were near-shore forms such as crocodiles, snakes and some turtles and they may have taken refuge in freshwater environments. A break in the food chain based on phytoplankton is proposed as an extinction scenario for pelagic forms. Article infos Published in Vol. 24, Fasc. 3-4 (1995) |
|
|
|
Pantolestidae nouveaux (Mammalia, Insectivora) de l'Eocène moyen de Bouxwiller (Alsace).Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Bouxwiller; Insectivora; Mammalia; Middle Eocene; Pantolestidaedoi: 10.18563/pv.3.3.63-82 Abstract The Pantolestidae from the middle eocene of Bouxwiller are the subject of a detailed study. Buxolestes hammeli (n. g., n. sp.) is not closely related to any other European or North American form described until now; it presents, however, some characters in common with Pantolestes, a form of the same age from North America. A parallel evolution from a common ancestral form could explain this ressemblance. Article infos Published in Vol. 03, Fasc. 3 (1970) |
|
|

|
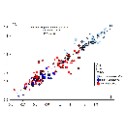
Un nouveau genre de ?Palaeotheriidae (Perissodactyla, Mammalia) décelé dans les phosphorites du Quercy (Eocène supérieur ou Oligocène) d'après un arrière crâne sans dents.Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: endocranial cast; Epitympanic sinus; Palaeotheriidae; Paléogène; Quercy Phosphorites; skull anatomyAbstract A rear skull from the Quercy Phosphorites is described. It documents a new perissodactyl genus, likely assignable to the family Palaeotheriidae and probably paleogene of age. Owing to the lack of any tooth, this family assignment remains however somewhat hypothetical. The specimen is firstly characterised by the presence of a wide epitympanic sinus swelling and hollowing the squamosal shell and the post-glenoid process. This cavity might make up a peculiar pattern of improvement for the hearing apparatus by carrying out a kind of drum near the middle ear, whereas the bony tympanic remains barely bulged and forms but a few developed auditory bulla. This pattern appears an outcome of a trend observed with many palaeotheriids, such as Plagiolophus. Furthermore, the endocranial cast shows a rather high degree of gyrencephaly for a paleogene mammal. The prominent lambdoidal crest points out a powerful nape musculature and a lowered head bearing. Consequently, it is assumed that such an animal was probably living in somewhat open places, at the expense of rather tough vegetables. It might have been accordingly provided with a semi-hypsodont, cement covered, "plagiolophoid" dentition. Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 1 (1999) |
|
|
|
Critical comments on the genus Propachynolophus Lemoine, 1891 (Mammalia, Perissodactyla, Equoidea)
|
|
S.I. Data |

|
Problems of classification as applied to the RodentiaAlbert E. WoodKeywords:Abstract A classification should be both usable and useful,not too complex either in the amount of splitting or in the number of hierarchies involved, and not so simple as to give a false assurance of knowledge of relationships. Classifications are only possible because we do not have complete knowledge of the evolution of the organisms concerned because gaps in the record are necessary to allow the separation of the various taxa. Rodent classification is complicated by the large number of organisms involved and by the geat amount of parallelism that has taken place in the evolution of any and all features. If several independent features are characteristic of a certain taxon, should an effort be made to define the group on the basis of all the features, or should only one be selected as the determinant ? Unless the evolution of the several features was closely linked, the former solution will sooner or later lead to insurmountable problems. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
Révision des Artiodactyles de l'Eocène moyen de Lissieu (Rhône)Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyles; Dichodon; FranceAbstract The object of this work is the study of the artiodactyls of the karstic locality of Lissieu near Lyon. Among the sixteen species counted, five (Hyperdichobune nobilis, Hyperdichobune sp., Haplabunodon mulleri, Tapirulus depereti and Pseudamphimeryx schlosseri) are cited for the first time in this fauna. The description of part of the anterior dentition of «Dichobune» langi permits the referal of this species to the genus Hyperdichobune. The new selenodont species Dichodon lugdunensis described in this work belongs, with its ancestor Dichodon simplex, to a lineage distinct from that of Dichodan cartieri and Dichodon ruetimeyeri. Finally, the taxonomic reality of the Lissieu species, Lophiobunodon rhodanicum Deperet, is justified. All the other species have been compared with those of Egerkingen. Even though with most of them no difference in age can be shown between the two deposits, some however indicate clearly by their degree of evolution that Lissieu is slightly more recent than Egerkingen. ln the history of Eocene mammals, the Lissieu fauna, because of its homogeneity, can be considered as a sure reference fauna of the Auversian period. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 4 (1972) |
|
|

|
Sur la présence de dents de mammifères (Creodonta, Perissodactyla) près de la limite Paléocène-Eocène à Hoegaarden, BelgiqueRichard Smith and Jerry J. HookerKeywords: Belgium; Creodonta; Landenian; Mammals; PerissodactylaAbstract Amongst a collection of selachian teeth made at Hoegaarden in a marine level of Bruxellian (Lutetian) age, containing a reworked Landenian (Sparnacian) fauna mixed with a contemporaneous one, a few teeth of terrestrial mammals have been discovered. They comprise two rare European taxa: ? Hallensia sp. and Palaeonictis gigantea, both known from the Landenian. Even though the ?Hallensia has not been definitely identified, il differs from the only perissodactyl of this age previously recorded from Belgium (Cymbalophus cuniculus). Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|