Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
Eocene Teleostean Otoliths, Including a New Taxon, from the Clinchfield Formation (Bartonian) in Georgia, USA, with Biostratigraphic, Biogeographic,
|
|
|

|
Analysis of changing diversity patterns in Cenozoic land mammal age faunas, South AmericaLarry G. Marshall and Richard L. CifelliKeywords: Cenozoic; Chronofaunas; diversity; Equilibrium theory; Extinction; Land mammal faunas; Origination; South AmericaAbstract Comparison of various measurements of taxonomic evolution using stratigraphic range data for orders, families and genera of land mammals indicates several means by which deficiencies of the South American fossil record (e.g., presence of hiatuses, unequal temporal and geographic representation of ages, unequal systematic treatment) may be normalized, thus permitting a less distorted appreciation of diversity pattern and trend. Initial radiation of native taxa resulted in a relative equilibrium by early Eocene time. Subsequent increases in absolute diversity were apparently induced by immigration at the family level and by environmental factors at the generic level. Miocene through Pleistocene phases of faunal stability, herein characterized as chronofaunas, are punctuated by rapid turnover events resulting from a complex of factors, including adaptive radiation of immigrant taxa into unoccupied eco-space; environmental and concomitant habitat change induced by orogenic events of the Andes; and biotic interactions between native and immigrant taxa, including competition and prey naivete. The first two factors account for major faunal transitions in the South American middle and late Tertiary; immigration-induced turnover may have been of greater importance in shaping the character of the fauna upon the Great American Interchange and the arrival of man in the Neotropics Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 4 (1990) |
|
|

|
Fossil snakes from the Palaeocene of São José de Itaboraí, Brazil Part III. Ungaliophiinae, Booids incertae sedis, and Caenophidia. Summary, update and discussion of the snake fauna from the localityJean-Claude RageKeywords: booid-grade incertae sedis; Brazil; Caenophidia; New taxa; Palaeocene; Russellophiidae; Snakes; tropidophiids; Ungaliophiinaedoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.37-73 Abstract Aside from Madtsoiidae, anilioids, and Boidae that were studied previously, the middle Palaeocene of ltaborai (BraziI) has produced Ungaliophiinae ("tropidophiids"), booid-grade snakes incertae sedis, and a possible Russellophiidae (Caenophidia) that are described in the present article. This article is the third and final report on the snakes from the locality. The Ungaliophiinae (Paraungaliophis pricei gen. et sp. nov.) are rare whereas the booid-grade snakes incertae sedis (ltaboraiophis depressus gen. et sp. nov., Paulacoutophis perplexus gen. et sp. nov.) are more frequent. A single vertebra is referred to the Russellophiidae (Caenophidia) with reservation. An update of the whole fauna of snakes from ltaborai is provided. Hechtophis austrinus that was tentatively referred to the erycine Boidae is now regarded as a Boidae incertae sedis. Most snakes from Itaborai are known only from the locality. Astonishingly, only the ailioids Coniophis cf. C. precedens gives possible evidence of interchanges between South and North America. The fauna of snakes from Itaborai, as well as the other Palaeocene faunas of snakes from South America are distinct from those of the Cretaceous and the Eocene of South America; they appear to be more different from the Cretaceous faunas than from those of the Eocene. The fauna from Itaborai is the richest and most diverse assemblage of snakes from the Palaeocene worldwide; it shares only a few taxa with other Palaeocene localities. Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|

|
New records of terrestrial Mammals from the upper Eocene Qasr el Sagha Formation, Fayum Depression, EgyptPatricia A. Holroyd, Elwyn L. Simons, Thomas M. Bown , Paul D. Polly and Mary J. KrausKeywords: Egypt; Eocene; Fossil mammals; Qasr el Sagha FormationAbstract New records of terrestrial mammals from the Qasr el Sagha Formation, Fayum Depression, Egypt are reported, and the stratigraphic occurrences of these fossils noted. These include additional specimens of Moeritheríum, Barytherium, and anthracotheres, as well as the oldest record of a hyracoid in the Fayum.These Eocene mammals occur almost exclusively in the alluvial deposits of the Dir Abu Lifa Member of the Qasr el Sagha Formation and show close affinities to the faunas from the lower sequence of the Jebel Qatrani Formation. There is no evidence of a more marked faunal discontinuity between the Qasr el Sagha and Jebel Qatrani Formations than there is across any of the three major breaks in sedimentation that exist within the Jebel Qatrani Formation. The faunal similarities between fossils of the lower sequence of the Jebel Qatrani Formation and of the upper part of the Qasr el Sagha Formation is consistent with recent paleomagnetic dating that suggests that these rocks differ in age by only one to two million years. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Difficulties with the origin of dinosaurs: a comment on the current debateMatthew G. BaronKeywords: dinosaur anatomy; dinosaur evolution; Ornithoscelida; palaeobiogeography; Triassic Perioddoi: 10.18563/pv.43.1.e3 Abstract The origin and early evolutionary history of the dinosaurs is a topic that has recently gone through a period of renewed interest and academic debate. For 130 years, one way of classifying the various dinosaur subgroups persisted as the accepted model, with increasing levels of research in the past quarter-century also providing evidence for the hypothesis that dinosaur origination occurred in the Southern Hemisphere, particularly in South America. It is, after all, from within the Late Triassic strata of countries like Argentina and Brazil that we get some of the very best early dinosaur specimens; many of these specimens are the earliest known representatives of some of the major dinosaur subgroups, such as the theropods and sauropodomorphs. However, some recent analyses have brought about a shift in terms of what is currently accepted and what is now disputed regarding the origin of dinosaurs – the Southern Hemisphere origination hypothesis was questioned (although this was based upon observations and not with quantitative analysis techniques), as has the shape of the dinosaur tree. Responses to the new hypothesis were numerous; many further supported a Southern Hemisphere point of origin. Whilst the interrelationships between the major dinosaur clades remains to be resolved, the current data does seem to comprehensively answer the question of where the dinosaurs first originated. However, it is arguable whether the current data that is being used in such palaeobiogeographical analyses is sufficient to provide an answer to the question of where specifically the dinosaur clade first appeared. This short communication urges a degree of caution about the current consensus and what steps may need to be taken to ensure that more meaningful results are produced in the future. Article infos Published in Vol 43-1 (2020) |
|
|

|
Revision of the family Cephalomyidae (Rodentia, Caviomorpha) and new cephalomyids from the early Miocene of Patagonia.Alejandro KramarzKeywords: Cephalomyidae; Lower Miocene; Patagonia; Rodentia; Soriamys; SystematicsAbstract A new genus of hystricognath rodent with two new species, Soriamys gaimanensis and Soriamys ganganensis, from the Colhuehuapian Age (Early Miocene), Sarmiento Formation, of Patagonia is described. The first species comes from the south barranca of the valley of Rio Chubut, near Gaiman locality (Chubut Province). It is known through a great number of dental remains in different stages of wear. The teeth are protohypsodont, with cement in the principal valleys. P4 are simpler, more oval inoutline and without a differentiated hypocone-hypoflexus. Upper molars are pentalophodont in early stages of wear and become bilobated in middle and advanced stages; M3 have a temporary third posterior lobe due to the maintenance of the braquiflexus on the posterior wall of the tooth. Lower teeth have a completely asymrnetrical pattern in relation to the uppers. The molars are trilophodont, with only one complex crest in the trigonid composed of the fusion of the anterolophid and mesolophid. The dp4 have a derived pentalophodont pattern due to the loss or fusion of the mesolophid and the development of an accessory transverse crest between the anterolophid and metalophid. The second species is known through a complete skull and jaw and other skull fragments with the dentition, proceeding from Pampa de Gan Gan, Chubut province. Respect to the first species, the teeth are higher crowned, with an earlier occlusal simplification and a third posterior lobe of M3 more developed and persistent. The skull and jaws show many chinchilloid characters, such as jugal bone with an ascending process, concave palate, very prominent dorsal shelf of the masseteric fossa, nasolachrymal duct opened laterally on the maxillary and very developed lateral mandibular fossa. Moreover, Soriamys is closely related to Cephalomys by sharing a similar asymmetric dental pattern and other dental and mandibular characters. These two genera constitute a natural group, the Cephalomyidae, with peculiar dental characters, like the asymmetric pattem of the upper and lower teeth; Cephalomyopsis, and probably Litadontomys, can be considered part of this group. Scotamys and Perimys constitute a distinct lineage (the Neopiblemidae or Perimyidae), more closely related to the chinchillids. Many characters shared by cephalomyids, eocardiids and caviids suggest a closer affinity between the Chinchilloidea and the Cavioiidea as a whole. Abrocoma shows also an asymmetric dental pattern and other chinchilloid features that suggest some degree of relationship with the cephalomyids, still not well determined. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 1-2 (2001) |
|
|

|
First record of the family Protocetidae in the Lutetian of Senegal (West Africa)Lionel Hautier, Raphaël Sarr, Fabrice Lihoreau, Rodolphe Tabuce and Pierre Marwan HamehKeywords: innominate; Lutetian; Protocetid; Senegaldoi: 10.18563/pv.38.2.e2 Abstract The earliest cetaceans are found in the early Eocene of Indo-Pakistan. By the late middle to late Eocene, the group colonized most oceans of the planet. This late Eocene worldwide distribution clearly indicates that their dispersal took place during the middle Eocene (Lutetian). We report here the first discovery of a protocetid fossil from middle Eocene deposits of Senegal (West Africa). The Lutetian cetacean specimen from Senegal is a partial left innominate. Its overall form and proportions, particularly the well-formed lunate surface with a deep and narrow acetabular notch, and the complete absence of pachyostosis and osteosclerosis, mark it as a probable middle Eocene protocetid cetacean. Its size corresponds to the newly described Togocetus traversei from the Lutetian deposits of Togo. However, no innominate is known for the Togolese protocetid, which precludes any direct comparison between the two West African sites. The Senegalese innominate documents a new early occurrence of this marine group in West Africa and supports an early dispersal of these aquatic mammals by the middle Eocene. Related dataset Article infos Published in Vol.38-2 (2014) |
|
|
|
New remains of the giant bird Gargantuavis philoinos from the Late Cretaceous of Provence (south-eastern France)Eric Buffetaut, Delphine Angst, Patrick Mechin and Annie Mechin-SalessyKeywords: Aves; Gargantuavis; Late Cretaceous; Pelvis; South-eastern Francedoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e3 Abstract
Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|
|
Palaeotis weigelti restudied : a small middle Eocene Ostrich (Aves : Struthioniformes)Peter Houde and Hartmut HauboldKeywords: Aves; Central Europe; Middle Eocene; Palaeotis; StruthioniformesAbstract Palaeotis weigelti, from the Middle Eocene of central Europe, is a flightless, paleognathous bird. It appears to be a member of the ostrich lineage on the basis of trivial derived characters. It is a very primitive ratite, however, and does not possess any of the highly specialized cursorial adaptations that characterize the modern steppe -and savanna- dwelling ostriches. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 2 (1987) |
|
|

|
The geologically youngest remains of an ornithocheirid pterosaur from the late Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous) of northeastern Mexico with implications on the paleogeography and extinction of Late Cretaceous ornithocheiridsEberhard D. Frey, Wolfgang Stinnesbeck, David M. Martill, Héctor E. Rivera-Sylva and Héctor Porras MúzquizKeywords: Coahuila; Late Cenomanian; north-eastern Mexico; Ornithocheiridae; Pterosauriadoi: 10.18563/pv.43.1.e4 Abstract Ornithocheirid pterosaurs were the largest of the toothed pterodactyloids and had a worldwide distribution, although their fossil record is fragmentary, with the exception of the north-eastern Brazilian Crato and Santana Formations (Aptian, ?Albian, Early Cretaceous). With Istiodactylidae, they were also the only toothed pterosaurs that survived into the Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous), becoming extinct at the end of this period. Here we report on an ornithocheirid metacapus from the Late Cenomanian laminated limestone of north-eastern Mexico discovered about 120 km north-west of Ciudad Acuña, northern Coahuila at the south banks of Rio Bravo. The specimen comprises a fragmentary distal syncarpal, a crushed but complete metacarpal IV, two fragmentary preaxial metacarpals and a possible fragmentary terminal left wing finger phalanx. It represents the geologically youngest known ornithocheirid worldwide. We suggest that ornithocheirid pterosaurs may have become extinct because of massive sea level fluctuations during the mid to late Cretaceous that may have obliterated their breeding sites on coastal plains and low lying islands. Article infos Published in Vol 43-1 (2020) |
|
|
|
Recherches de mammifères paléogènes dans les départements de l'Aisne et de la Marne pendant la deuxième moitié du vingtième sièclePierre LouisKeywords: Biochronology; Eastern Paris Basin; Fossil localities; Mammals; paleoenvironments; Paléogène; PaleogeographyAbstract A brief historical account of fossil vertebrate discoveries in the Eastern part of the Paris Basin between the beginning of the nineteenth century and 1950 is given. Other localities discovered since then are presented. A reconstruction of past landscapes is briefly elaborated. A biozonation based on mammals is proposed, from the Late Thanetian to the Middle Bartonian. Paleogeographical considerations are added. Suggestions regarding the search for new marnmal localities are made. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
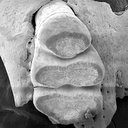
|
A new Desmodillus (Gerbillinae, Rodentia) species from the early Pliocene site of Langebaanweg (South-western Cape, South Africa)
|
|
S.I. Data |

|
Long-term fidelity of megaoolithid dinosaurs to a large breeding-ground in the Upper Cretaceous of Aix-en-Provence (southern France).Géraldine Garcia, Yves Dutour, Isabellle Cojan, Xavier Valentin and Gilles CheylanKeywords: Large nesting ground; megaloolithid eggs; Southern France; Upper CretaceousAbstract We present here the preliminary results from a new nesting site "Sextius-Mirabeau", discovered close to the historical centre of Aix-en-Provence in Upper Cretaceous deposits. This extensive megaloolithid nesting ground, the first large scale excavation (3225 m²) in France, yielded more than 530 eggs, some organized in clusters. Their study reveals the reproductive strategy of the megaloolithid egglayer group which indicates nesting fidelity and gregarious behaviour. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|
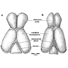
|
The endocranial cast and encephalization quotient of Ptilodus (Multituberculata, Mammalia)David W. Krause and Zofia Kielan-JaworowskaKeywords: encephaIization quotient; endocranial cast; Montana; Multituberculata; olfactory bulbs; Paleocene; PtilodusAbstract Simpson (1937a) reconstructed the brain of the Paleocene multituberculate Ptilodus as having the olfactory bulbs widest anteriorly, an unusual condition among mammals. Slight preparation and reexamination of the endocast specimens of Ptilodus reveals that the olfactory bulbs in fact taper anteriorly, as in the recently-described endocranial casts of three multituberculate species from the Late Cretaceous of Asia, and as in those of other mammals. The brain of Ptilodus was therefore essentially of the same general pattem as in other multituberculates. Ptilodus differs, however, in having the vermis more deeply inserted between the cerebral hemispheres. Other details concerning the endocast morphology of Ptilodus are clarified. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|

|
A reassessment of the giant birds Liornis floweri Ameghino, 1895 and Callornis giganteus Ameghino, 1895, from the Santacrucian (late Early Miocene) of Argentina.Eric BuffetautKeywords: Argentina; Aves; Callornis; Liornis; Miocenedoi: 10.18563/pv.40.2.e3 Abstract The status of the giant bird taxa Liornis floweri and Callornis giganteus from the Santa Cruz Formation (late Early Miocene) of Patagonia, first described by Ameghino (1895) is reassessed on the basis of a re-examination of the type material at the Natural History Museum, London. Liornis floweri, which lacks a Pons supratendineus on the tibiotarsus and has an unbifurcated Canalis interosseus distalis on the tarsometatarsus, is clearly a brontornithid and is considered as a junior synonym of Brontornis burmeisteri. Ameghino’s replacement of Callornis by Eucallornis is unjustified. Callornis giganteus is a chimera based on a phorusrhacid tarsometatarsus (probably belonging to Phorusrhacos longissimus) and a brontornithid tibiotarsus. The latter can be considered as the lectotype of Callornis giganteus, which may represent a small morph of Brontornis burmeisteri or a distinct taxon. It is referred to here as Brontornithidae indet. The tarsometatarsus described by Dolgopol de Saez (1927a,b) as Liornis minor and considered by her as a gracile brontornithid apparently has a bifurcated Canalis interosseus distalis and should therefore be placed among the Phorusrhacidae. Article infos Published in Vol.40-2 (2016) |
|
|
|
Paleogene faunal assemblage fron Antofagasta de la Sierra (Catamarca Province, Argentina).Guillermo M. LopezKeywords: Argentina; Faunal assemblage; Mammalia; Middle Eocene; ReptiliaAbstract The Paleogene faunal assemblage from Antofagasta de la Sierra (Catamarca, Argentina), is here presented, both in its geological and systematic aspects. The fossil bearing levels are referred to the Geste Formation (Pastos Grandes "Group"). The described specimens belong to the Classes Reptilia (Orders Crocodylia, Serpentes and Chelonii) and Mammalia (three taxa from the Superorder Marsupialia, representatives of the Orders Edentata, Condylarthra, Pyrotheria and Astrapotheria, and six families of the Order Notoungulata). This fauna is referred to the Mustersan Age, which in Patagonia represents the Middle Eocene. Such chronologic assignment is based on the presence of characteristic taxa, their evolutionary stage and on stratigraphic evidence. Finally, a brief comparison with other faunal assemblages from the Early Tertiary of Argentina and Chile, is presented. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|

|
A new rodent from Quaternary deposits of the Canary Islands and its relationships with Neogène and recent murids of Europe and Africa.Rainer Hutterer, Nieves Lopez-Martinez and Jacques MichauxKeywords: Canary Islands; Holocene; Island evolution; Muridae; PHYLOGENY; Rodents; SpainAbstract A peculiar new rodent, Malpaisomys insularis nov. gen., nov. sp., is described from subfossil deposits of the eastern Canary Islands. The species shows some highly specialized skull features although its molars exhibit a mixture of primitive and derived characters among which a partial stephanodonty is most notable. A comparison of the new rodent with several Miocene to Holocene Muridae shows that Malpaisomys possibly shares a common ancestor with Acomys and Uranomys. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Fasc. 4 (1988) |
|
|

|
La morphologie dentaire des Thalattosuchia (Crocodylia, Mesosuchia).Patrick VignaudKeywords: Dental morphology; Dental types; feeding habits.; Jurassic; Metriorhynchidae; Systematics; Teleosauridae; ThalattosuchiaAbstract The tooth morphology of the Thalattosuchia (marine crocodilians from the Jurassic and the Early Cretaceous) is analysed. The Callovian from Poitou and the Kimmeridgian from Quercy have yielded many remains of Metriorhynchus, Steneosaurus and Machimosaurus. These remains allow us to study the variations of tooth morphology during ontogenic growth, tooth replacement and the location of the teeth. We have defined different tooth types for these genera. In Metriorhynchus, the two tooth types defined do not coincide with the two groups recognized in the Callovian (broad-skulled and narrow-skulled metriorhynchids) but reflect the prey preferences of these forms. In Steneosaurus and Machimosaurus the five tooth types deñned are in agreement with the main taxa known from the Bathonian to the Early Cretaceous. This study allows to precise the function and the prey preference of the Thalattosuchia during the Jurassic and the Early Cretaceous. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|
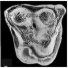
|
Artiodactyla from the early Eocene of KyrgyzstanAlexander AverianovKeywords: Artiodactyla; Asia; Diacodexeidae; Eocene; KyrgyzstanAbstract Isolated upper cheek teeth of the primitive artiodactyl Diacodexis sp., upper molars of Eolantianius russelli gen. et sp. nov. (Diacodexeidae), two lower molars tentatively referred to Eolantianius russelli gen. et sp. nov., and astragali of Diacodexeidae indet. are described from the early Eocene (late Ypresian) of locality Andarak 2 in Kyrgyzstan. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Pronycticebus neglectus - an almost complete adapid primate specimen from the Geiseltal (GDR)Urs Thalmann, Hartmut Haubold and Robert D. MartinKeywords: Adapiformes; Eocene; Paleoecology; PHYLOGENY; Pronycticebus neglectusAbstract In the course of the current revision of adapid primates from the Eocene Geiseltal, an almost complete specimen was found in the Geiseltal Museum collections. The fossil, the most complete adapid specimen so far discovered in Europe, has been determined as Pronycticebus neglectus n. sp. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|