Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Rodent paleocommunities from Ulantatal
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
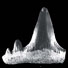
Discovery of the most ancient Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand. New considerations on the systematics and range of the genus
|
|
|
|
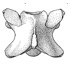
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)Gerard R. Case and Henri CappettaKeywords: Elasmobranchs; New Jersey; new species; Upper Cretaceous; USAAbstract A recently discovered, almost complete specimen of a hybodont tooth, allows us to describe as a new species, fairly common, but usually fragmentary teeth in the Navesink Formation of New Jersey: Hybodus novojerseyensis nov. sp. Article infos Published in Vol. 33, Fasc. 1-4 (2004) |
|
|
|
Fossil snakes from the Palaeocene of Sao José de Itaborai, Brazil.Part 1 Madtsoiidae, Aniliidae.Jean-Claude RageKeywords: Aniliidae s.l.; Brazil; Coniophis; Hoffstetterella; Madtsoia; Madtsoiidae; middle Palaeocene; New taxa; SnakesAbstract The middle Palaeocene of São José de Itaboraí (State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) has yielded a very rich and diverse snake fauna which includes Madtsoiidae, Aniliidae s.l., Boidae, Tropidophiidae s.l., Booidea incertae sedis, and Russellophiidae. The present article (part I) deals with Madtsoiidae and Aniliidae s.l. Madtsoiidae are represented by many vertebrae and a few skull bones. They comprise one new species assigned to the genus Madtsoia (M. camposi sp. nov.). However, the definition of the genus Madtsoia is unsatisfactory and the generic allocation might be provisional. A few elements, vertebrae only, belong to the Aniliidae s. l. Two taxa are referred to this latter group: Coniophis cf. C. precedens and Hoffstetterella brasiliensis gen. et sp. nov. The forthcoming part II will deal with Boidae. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 3-4 (1998) |
|
|

|
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the European Association of Vertebrate Palaeontologists (EAVP), 5-9 July 2021, Benevento, ItalyMatteo Belvedere, Verónica Díez Díaz and Raffaele SardellaKeywords: 2021; Benevento; EAVPdoi: 10.18563/pv.eavp2021 Abstract Welcome to the 18th conference of the EAVP, the first online meeting of our association. The pandemic emergency made it impossible to organize the in-person meeting in Benevento as we all had hoped. However, we couldn’t miss another EAVP meeting. Therefore, this year we are meeting online, trying to make the experience the closest to the in-person meeting possible, in order to offer the delegates the opportunity to share knowledge, build new networks and reinforce the old ones. We have received 137 communications, with more than 150 delegates from 24 countries. All the abstracts have passed a peer review process and are part of this special volume of Palaeovertebrata, the official journal of the EAVP. This year we are also offering a variety of workshops, roundtables and symposia on different topics. These include the annual “Pride EAVP: An LGBTQ+ Roundtable” and “Women in Palaeontology Roundtable Discussion”, together with the workshops on “Gendered Perspective in Palaeontological Research: from Definition to Action”, “International Palaeontology Education: Virtual Teaching and Real-World Learning”, “Stepping out of Academia: Why, When and How?”, “Introduction to Hypothesis Testing in Statistics”, “The Early-Middle Pleistocene Transition: Marked Mammal Turnover and Ecosystem Dynamic” (included in the early event for the XXI INQUA Congress in Rome 2023, “A Mediterranean Perspective on Quaternary Sciences”). To conclude, we are hosting two symposia on “Palaeoart: Diversity on and behind the Canvas” and “3D fossils, Robotic and Experimental Palaeontology”. We wish you all a happy and productive meeting. And see you in Benevento next year! Article infos Published in Special Volume 1-2021 (2021) |
|
|
|
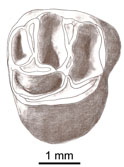
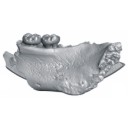
Rodent paleocommunities from the Oligocene of Ulantatal (Inner Mongolia, China)Helder Gomes Rodrigues, Laurent Marivaux and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: late Paleogene; Mammalia; Mongolian Plateau; Rodentia; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.38.1.e3 Abstract The Oligocene deposits of the Ulantatal area in Inner Mongolia (China) contain among the richest mammalian faunas from Asia. To date, only some parts of the rodent faunas have been described. Here, we propose to review the rodent faunal lists for each site, including the description of a few new rodent specimens. We describe three additional rodent species: the Cylindrodontidae Anomoemys lohiculus, the Eomyidae Asianeomys sp., and the Dipodidae Litodonomys huangheensis. This study allows us to constrain the stratigraphic range of Anomoemys lohiculus, which ranged from the late Early Oligocene to the early Late Oligocene in this area. Asianeomys sp. and Litodonomys huangheensis are dated from the latest Oligocene. These Oligocene deposits consist now of more than 70 species of mammals if we include the fauna from Kekeamu. This latter corresponds to the basal part of the Ulantatal Formation and could be dated biochronologically from the earliest Oligocene. When compared to the faunas from the Valley of Lakes in Central Mongolia, the Ulantatal faunas present a great majority of rodents, and this difference can be partly explained by sampling and description biases regarding macro-mammals. This study also shows that variations existed between Inner and Central Mongolia, especially regarding the composition of the rodent paleocommunities. However, the assessment of their evolutionary history in this part of Asia with respect to the important climate and environment changes, require further precisions and more material than current data allow. Article infos Published in Vol.38-1 (2014) |
|
|
|
Enigmatic rodents from Lavergne, a late middle Eocene (MP 16) fissure-filling of the Quercy Phosphorites (Southwest France)
|
|
|
|
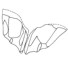
A new species of chimaeroid fish from the upper Paleocene (Thanetian) of Maryland, USAGerard R. CaseKeywords: Chimaeroid nov. sp.; Maryland; U.S.A.; Upper PaleoceneAbstract The recent discovery of several mandibular toothplates of a chimaeroid fish at a dig in the area of the Landover Mall, near Landover, Prince Georges County, Maryland, brings to our attention a new species of the chimaeroid, Ischyodus. Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Fasc. 1-2 (1991) |
|
|

|
Stratigraphy and Oligocene-Miocene mammalian biochronology of the Aktau Moutains, Dzhungarian Alatau Range, KazakhstanElena G. Kordikova and Alexander V. MavrinKeywords: Dzhungarian Alatau; Kazakhstan; Lithologic correlation; Mammalian biochronology; Miocene; Oligocene; StratigraphyAbstract Stratigraphic studies in the Aktau Mountains bordering the Dzhungarian Alatau Range in southeastern Kazakhstan have included mapping of Tertiary lithostratigraphic units, documentation of fossiliferous deposits, correlation of sections, etc. These investigations have led in turn to revised interpretation of the Tertiary geology of the area. The Tertiary sequence in the Aktau Mountains is represented by three lithostratigraphic units (in ascending order): (1) the middle Eocene Akbulak Formation; (2) the Oligocene Aktau Formation with a lower member including white quartz sands that contain fossil mammals, and an upper member including red-colored clays and sandstones, brick red clays, an anhydrite and gypsum clayey horizon, and bright brown-red clays; and (3) the upper Oligocene-Miocene Chul'adyr Formation with a lower member of greenish and yellowish conglomerates and gritstones, a middle member including grayish and yellowish sands and gritstones, and an upper member including brown and red clays and carbonate- and anhydrite-rich clays. The Aktau and Chul”adyr Formations represent separate cycles of sedimentation. Mammalian biostratigraphy and biochronology of the three vertebrate faunas in Aktau Mountains are reviewed. The mammalian fauna from white sands of the lower Aktau Formation is small but includes Ardynia and is thought to be early Oligocene in age. The mammalian fauna from conglomerates and gritstones of the lower member of the Chul”adyr Formation is also small but includes Paraceratherium and is thought to be late Oligocene in age. The mammalian fauna from sands of the middle member of the Chul'adyr Formation is extensive, with micro- and macrofauna attributed to Neogene mammal zones MN4 to MN 6, indicating a latest early Miocene to earliest middle Miocene age (Orleanian-Astaracian). Most genera of middle Chul”adyr mammals are known from the middle Miocene Shanwang faunas of China and from the Castelnau-d”Arbieu faunal assemblage (MN4-MN6) of southwestern France. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
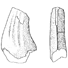
The Late Cretaceous nesting site of Auca Mahuevo (Patagonia, Argentina): eggs, nests, and embryos of titanosaurian sauropods.Luis M. Chiappe, Rodolpho. . Coria, Frankie D. Jackson and Lowell DingusKeywords: Argentina; Eggs; embryos; Late Cretaceous; nests; Patagonia; titanosaurian sauropodsAbstract The late Cretaceous Auca Mahuevo nesting site (Neuquén Province, Argentina) has produced a large number of sauropod eggs, many of them containing the remains of embryos. Research at this site has generated important information about the development of the embryos, the morphology and eggshell microstructure of the eggs, and the reproductive behavior of sauropod dinosaurs. Cranial features present in the embryos have allowed their identification as those of titanosaurian sauropods. Differences in the texture of the sediments that contain some of the egg-clutches have illuminated their nest architecture. Microstructural studies of eggshells have expanded our knowledge of their variability and the incidence of pathologies within a reproductive titanosaurian population. Maps showing the spatial distribution of eggs and clutches. the stratigraphic distribution of the egg-beds, and the sedimentological context in which they are contained, have provided the basis for several inferences about the nesting behavior of these dinosaurs. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|
|
First record of dinosaur eggshells and teeth from the north-west african Maastrichtian (Morocco).Géraldine Garcia, Rodolphe Tabuce, Henri Cappetta, Bernard Marandat, Ilhem Bentaleb, Aziza Benabdallah and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Africa; amniotic eggshells; Maastrichtian; Morocco; theropod teethAbstract We report the discovery of amniotic eggshells and theropod teeth from the Late Cretaccous period in Morocco.The megaloolithid family represents the only known dinosaur egg remains in the north part of Africa and attests indirectly to the occurrence of sauropod dinosaurs (titanosaurids) in the Maastrichtian of Africa. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|

|
Angolabatis nom. nov.,a replacement name for the Cretaceous genus Angolaia Antunes & Cappetta, 2002 (Chondrichthyes: Rajiformes), a preoccupied name.Miguel T. Antunes and Henri CappettaKeywords: Angola; Campanian/Maastrichtian; homonymy; Hypsobatidae; nomen novum; RajiformesAbstract In 2002, Antunes & Cappetta published several new taxa (genera and species) in a paper on Cretaceous elasmobranch faunas from Angola. One of the new genera was named Angolaia (Rajiformes, Hypsobatidae; type-species: Angolaia benguelaensis Antunes & Cappetta, 2002, Late Campanian/Early Maastrichtian of Angola). Recently, Dr. Christian Kammerer kindly informed us that the genus Angolaia was preoccupied by a cicadellid homoptere (Insecta), published by Linnavuori & Al-Ne'amy, 1983. So, according to mIes of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN 1999, articles 52, 60) this name became unavailable. Consequently, the Rajiformes genus Angolaia is a junior homonym, invalid and must be rejected. In replacement, we propose the new name Angolabatis. Article infos Published in Vol. 34, Fasc. 1-2 (2006) |
|
|

|
Diversity among north african dinosaur eggshells.Monique Vianey-Liaud and Géraldine GarciaKeywords: Cretaceous; Dinosaurs diversity; Eggshells; Maastrichtian; Morocco; North Africa; taxonomyAbstract Until the discovery of dinosaur eggshells locality in the Oukdiksou syncline, (Middle Atlas, Morocco) in 1999 (Garcia et al. this volume) the maastrichtian reptiles faunas were unknown in North Africa. Additional material from Achlouj-2 allows us to describe five oospecies, belonging to four oofamilies. The Megaloolithidae is recorded by Megaloolithus maghrebiellsis Garcia el al. and Pseudomegaloolithus atlasi oogen. novo oospec. nov. Tipoolithus achloujensis Garcia et al. is questionably considered as a Subtiliolithidae. A relatively small Elongatoloolithidae is represented by Rodolphoolithus arioul oogen. nov. oospec. nov. A thin Prismatoolithidae is described as a new oospecies of ? Pseudogeckoolithus Vianey-Liaud & Lopez-Martinez, 1997: P. tirboulensis. The diversity of these oospecies indicates that the dinosaur fauna comprises at least five dinosaur oospecies, with perhaps one sauropod and three theropods. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|

|
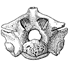
Pterosaurs (Pterosauria) from the Cerro del Pueblo Formation (Late Campanian) of Coahuila, MexicoHector Rivera-Sylva, David Hone, Martha Aguillón-Martínez, Rubén Guzmán-Gutiérrez, David Morales-Flores, Iván . Sánchez-Uribe, José Flores-Ventura and Rafael Vivas-GonzálezKeywords: Azhdarchoidea; Coahuila; Mexico; Pterodactyloidea; Pterosauriadoi: 10.18563/pv.48.2.e1 Abstract The Late Campanian Cerro del Pueblo Formation, located in southeastern Coahuila, Mexico, has produced a diverse array of vertebrate fossils. However, pterosaur remains from this unit are notably scarce. In this study, we describe new pterosaur material from the formation. The specimens include a fragmentary vertebra identified as belonging to an indeterminate, but derived pterodactyloid, along with the distal condyle of a left metacarpal, referable to an azhdarchoid pterosaur, and a left manus print. While these specimens provide additional evidence of pterosaur presence in the region during the Late Cretaceous, their fragmentary nature limits precise taxonomic and ichnotaxonomic identification. Nevertheless, they highlight the potential for future discoveries that could refine our understanding of the diversity and distribution of pterosaurs in Mexico. Article infos in press |
|
|
|
Fossil snakes from the Palaeocene of Sao José de Itaborai, Brazil, Part II. BoidaeJean-Claude RageKeywords: Boidae; Boinae; Brazil; Erycinae; New taxa; Palaeocene; SnakesAbstract The middle Palaeocene of São José de ltaboraí (State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) has produced a rich and diverse fauna of boid snakes. It comprises six or seven species: Hechtophis austrinus gen. et sp. nov., Corallus priscus sp. nov., Waincophís pressulus sp. nov., Waincophis cameratus sp. nov.,"Boinae A", and "Boinae B". Moreover, two dentaries might pertain to either H. austrinus or "Boinae B", or even represent a distinct taxon. Hechtophis austrinus is assigned, with reservation, to the Erycinae. All other taxa are referred to the Boinae. The vertebrae of all taxa have paracotylar foramina, which raises the problem of the apomorphic or plesiomorphic nature of this feature. This fauna also raises the question of the presence of extinct erycine boids in South America, but it does not allow this question to be settled. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 3-4 (2001) |
|
|

|
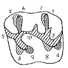
Archosauriform teeth from the upper Triassic of Saint Nicolas-de-Port (Northeastern France).Pascal Godefroit and Gilles CunyKeywords: Archosauriforms; Graoullyodon hacheti; Saint-Nicolas-de-port; Teeth; Upper TriassicAbstract The Late Triassic locality of Saint-Nicolas-de-Port (Meurthe-et-Moselle, France) has yielded numerous isolated teeth belonging to archosauriform reptiles. The following tooth groups can be identified: heterodont phytosaurs, the pterosaur Eudimorphodon, the prosauropod dinosaur Plateosaurus, three types of putative ornithischian teeth and 13 types of carnivorous Archosauriformes indet. Apparent venom-conducting teeth belonging to a new taxon of ?Archosauriformes (Graoullyodon hacheti nov. gen. nov. sp.) are also described. From a palaeogeographical point of view, the ornithischian teeth from Saint-Nicolas-de-Port (if their attribution is confirmed) are the oldest fossils of this group in Europe. The biostratigraphic distribution of the tooth forms mostly suggests a Late Norian or Early Rhaetian (depending on current interpretations) age of the deposits, but do not provide more precisions than fossils previously described from the area. The dietary habits and, consequently, the palaeoecological relationships of the different vertebrate groups discovered at Saint-Nicolas-de-Port are tentatively established: the ornithischian and prosauropod teeth reflect a herbivorous diet, whereas the other archosauriform teeth are probably from camivores or omnivores. Article infos Published in Vol. 26, Fasc. 1-4 (1997) |
|
|
|
Functional aspects of the evolution of rodent molarsPercy M. ButlerKeywords: Chewing; Muridae; Rodents; Wear facetsAbstract The wear facets of primitive rodents can be homologized with those of primitive primates and ungulates. As in primates, the jaw movement was ectental, with an increased anterior component in the lingual phase (phase ll). The buccal phase (phase I) in rodents approaches the horizontal and it tends to be reduced in importance in comparison with the lingual phase. ln more advanced rodents the efficiency of grinding is increased by the development of additional cutting edges of enamel (e.g. enlargement of hypocone, development of mesoloph and lingual sinus). The buccal phase movement becomes lined up with the lingual phase movement to form a single oblique chewing stroke,resulting in planation of the crown. As the stroke becomes more longitudinal (propalinal) the enamel edges become more transverse. In Muridae propalinal chewing evolved before the loss of cusps, facets were reorientated and additional cusps developed. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
There were giants upon the earth in those daysPierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: Eurasia; history of science; Indricotheriinae; Paléogène; Rhinocerotoideadoi: 10.18563/pv.38.1.e4 Abstract Rhinoceros Giants: the Paleobiology of Indricotheres. Donald R. Prothero. Life of the Past Collection, Indiana University Press; 160 pp. (66 b&w illustrations). Hardback (7x10”): USD 42.00 plus shipping. ISBN: 978-0-253-00819-0. E-book: USD 34.99. ISBN: 978-0-253-00826-8. Article infos Published in Vol.38-1 (2014) |
|
|

|
New late Paleocene rodents (Mammalia) from Big Multi Quarry, Washakie Basin,Wyoming.Mary R. Dawson and Christopher K. BeardKeywords: Clarkforkian; North America; Paleocene; RodentiaAbstract The earliest North American rodents occur in basal Clarkforkian beds of the Fort Union Formation at Big Multi Quarry near Bitter Creek, northern Washakie Basin, Sweetwater County, Wyoming, and in closely correlative Fort Union beds formerly accessible in the Eagle Coal Mine near Bear Creek, northern Clark's Fork Basin, Carbon County, Montana. Two new species of early Clarkforkian rodents, Paramys adamus and Alagomys russelli, are described from Big Multi Quarry. Paramys adamus is represented by virtually complete upper and lower dentitions, which demonstrate that this species is one of the most primitive North American paramyids yet discovered. These specimens form the basis for a reevaluation of the content and stratigraphic range of P. atavus, which is known with certainty only from Bear Creek. Alagomys russelli is the first North American record for the enigmatic rodent family Alagomyidae, otherwise known from ?late Paleocene-early Eocene localities in Mongolia and China. Phylogenetic analysis of dental and gnathic traits suggests that Alagomyidae form the sister group of all other undoubted rodents. At least two rodent clades, alagomyids and basal paramyids, seem to have invaded North America from Asia at the beginning of Clarkforkian time, but only the paramyids persisted to undergo a significant evolutionary radiation in North America. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
Dating dinosaur oodiversity: chronostratigraphic control of LateCretaceous oospecies succession.Nieves Lopez-MartinezKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Chronology; dinosaur eggshells; Late CretaceousAbstract An increasing fossil record of dinosaur eggs and eggshells allows putting ootaxa within a chronostratigraphic framework, in order to study their distribution pattern leading eventually to their use as biochronological markers. For these purposes, high-quality data exists in four major regions; North America, South America, Europe and Asia (Central Asia and India). Most of the highly diverse dinosaur egg record has been dated as Latest Cretaceous in age (Campanian-Maastrichtian), reaching the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary closer than the dinosaur bone record. However, dating continental sections is problematic and need to be carefully verified, as it appears when comparing the European dinosaur eggshell record from two well-studied areas. Ootaxa distribution in both sides of the Pyrenees (Tremp and Aix basins) shows comparable oospecies successions, but different chronology. This disagreement probably indicates that one or both successions have a wrong chronostratigraphic calibration. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|
|

|
Historical and new perspectives on the parataxonomyof fossil eggs.Monique Vianey-Liaud and Darla ZelenitskyKeywords: amniotic eggshells; ParataxonomyAbstract A critical review on the literature about the parataxonomy of amniote eggshells reasserts the great interest of this systematics tool for the progress of dinosaur eggshell paleontology. However, shedding light on its limits, we propose to give up the use of the basic types - morphotypes key system. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 2-4 (2003) |
|