Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
Diversity of triconodont mammals from the early Cretaceous of North Africa-affinities of the AmphilestidsDenise Sigogneau-RussellKeywords: amphilestines; Early Cretaceous; gobiconodontines; North Africa; Teeth; triconodontsAbstract The mammalian fauna (represented only by isolated teeth) from the early Cretaceous of Morocco includes a number of non-'therian' specimens, characterized by the antero-posterior alignement of the main molar cusps. This assemblage is very heterogenous, including forms (among them Gobiconodon palaios sp. nov.) that can be related to Laurasian triconodonts and several forms so far known only in this part of Gondwana (among them Kryptotherium polysphenos gen. et sp. nov.). The latter, in particular, exemplifies the diversity of the mammalian dental morphology in the Mesozoic, often largely underestimated. In the last part of this paper, the 'therian' affinity of the 'amphilestids' is discussed, on the basis of the arrangement of molar cusps, the interlocking mechanism and the occlusal pattem. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 1 (2003) |
|
|

|
Une nouvelle espèce de Steneosaurus (Thalattosuchia, Teleosauridae) dans le Callovien du Poitou (France) et la systématique des Steneosaurus longirostres du Jurassique moyen d'Europe Occidentale.Patrick VignaudKeywords: middle Jurassic; nov. sp.; phylogenetic relationships; skulls; Steneosaurus pictaviensis; Systematics; thalattosuchian crocodileAbstract The study of all the available skulls allows us to review the systematic relationships of the longirostrine Steneosaurus from the Middle Jurassic of western Europe. Up to now, Aalenian and Bajocian deposits have not yielded any significant Steneosaurus remain. In the Bathonian, the only valid longirostrine species, S. megistorhynchus, is known in the Britain-Normandy Basin, the Poitou and the Lorraine. In the Callovian, most of the longirostrine Steneosaurus remains can be attributed to the species S. leedsi. Nevertheless, some remains from the Middle Callovian of Poitou (France) show important differences with S. leedsi. A new Steneosaurus species, only known in Poitou, is created and named S. pictaviensis. The specific characters are carried by the skull (preorbital pit well marked, orbit and ptetygoid fossae shapes), by the mandible (symphysis shape) and by the teeth (ornamentation). S. megistorhynchus is probably situated near the stem of the Callovian species but remains from the Bathonian and Lower Callovian are very scarce and it is very difficult to precise the phylogenetic relationships between the longirostrine species of the Middle Jurassic. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 1-2 (1998) |
|
|

|
Difficulties with the origin of dinosaurs: a comment on the current debateMatthew G. BaronKeywords: dinosaur anatomy; dinosaur evolution; Ornithoscelida; palaeobiogeography; Triassic Perioddoi: 10.18563/pv.43.1.e3 Abstract The origin and early evolutionary history of the dinosaurs is a topic that has recently gone through a period of renewed interest and academic debate. For 130 years, one way of classifying the various dinosaur subgroups persisted as the accepted model, with increasing levels of research in the past quarter-century also providing evidence for the hypothesis that dinosaur origination occurred in the Southern Hemisphere, particularly in South America. It is, after all, from within the Late Triassic strata of countries like Argentina and Brazil that we get some of the very best early dinosaur specimens; many of these specimens are the earliest known representatives of some of the major dinosaur subgroups, such as the theropods and sauropodomorphs. However, some recent analyses have brought about a shift in terms of what is currently accepted and what is now disputed regarding the origin of dinosaurs – the Southern Hemisphere origination hypothesis was questioned (although this was based upon observations and not with quantitative analysis techniques), as has the shape of the dinosaur tree. Responses to the new hypothesis were numerous; many further supported a Southern Hemisphere point of origin. Whilst the interrelationships between the major dinosaur clades remains to be resolved, the current data does seem to comprehensively answer the question of where the dinosaurs first originated. However, it is arguable whether the current data that is being used in such palaeobiogeographical analyses is sufficient to provide an answer to the question of where specifically the dinosaur clade first appeared. This short communication urges a degree of caution about the current consensus and what steps may need to be taken to ensure that more meaningful results are produced in the future. Article infos Published in Vol 43-1 (2020) |
|
|
|
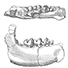
Les mammifères de Rians (Eocène inférieur, Provence)Marc GodinotKeywords: Eocene; Mammals; Provence; RiansAbstract The fossil mammals discovered in the quarry of Rians (Sparnacian, Provence) are described. Among these forms, Hyracotherium is interesting because of the little molarization of the lower premolars and its small size, and Diacodexis by its small size and very primitive astragalus ; they may be the most primitive representatives of their respective orders. Also, Proviverra eisenmanni n. sp. is the smallest and most primitive hyaenodontid yet described. Hyopsodus itinerans is the first species of this genus described France. Among other rare fossils is a new species of bat, a small palaeoryctid, and other forms not yet identified. Marsupials are varied. Several new species are present among the rodents. The fauna is well-balanced and rich in small hyopsodontid condylarths. It is stratigraphically situated at the Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 2 (1981) |
|
|
|
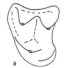
Dilambodont Molars :a functional interpretation of their evolutionPercy M. ButlerKeywords: Convergent evolution; Dilambdodont; Molar function; Molar teethAbstract In dilambdodont molars the primitive crest between paracone and metacone (centrocrista) is represented by a pair of crests that join the mesostyle (postparacrista, premetacrista). The cutting action of these crests against the crests of the hypoconid is described. Dilambdodonty is a derived adaptation for greater cutting efficiency. It has evolved several times and in more than one way. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
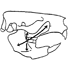
Schmelzmikrostruktur in den inzisiven alt-und neuweltlicher histricognather nagetiereThomas MartinKeywords: Africa; Caviomorpha; Ctenodactyloidea; Deseadan; Enamel microstructure; Hunter-Schreger bands; Hystricognathi; Incisors; Ischyromyoidea; multiserial; Paleobiogeography; pauciserial; Phiomorpha; Rodentia; South AmericaAbstract Enamel microstructure in the incisors of Old- and New World hystricognath rodents: Article infos Published in Vol. 21, Ext (1992) |
|
|

|
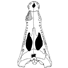
Pronycticebus neglectus - an almost complete adapid primate specimen from the Geiseltal (GDR)Urs Thalmann, Hartmut Haubold and Robert D. MartinKeywords: Adapiformes; Eocene; Paleoecology; PHYLOGENY; Pronycticebus neglectusAbstract In the course of the current revision of adapid primates from the Eocene Geiseltal, an almost complete specimen was found in the Geiseltal Museum collections. The fossil, the most complete adapid specimen so far discovered in Europe, has been determined as Pronycticebus neglectus n. sp. Article infos Published in Vol. 19, Fasc. 3 (1989) |
|
|
|
Lower Paleogene crocodilians from Silveirinha, Portugal.Miguel T. AntunesKeywords: ?Upper Paleocene / Lowermost Eocene; Crocodilians; Ecology; PortugalAbstract The presence at Silveirinha of one of the earliest, ? Late Paleocene or Lowermost Eocene, european representatives of the genus Diplocynodon is based mostly on isolated bones and teeth (often from juveniles). This small-sized form is the only crocodilian so far recognized in this site. The longevity of Diplocynodon in Portugal becomes much extended; the genus survived there until the Middle Miocene at least. A discussion on the possible affinities with other eocene Díplocynodon and especially those from Cubillos-Valdegallina (Zamora, Spain) is presented. On the other hand, differences have been detected in comparison with: Díplocynodon tormis, from the middle Eocene of the Douro basin in Spain, which may belong to another phyletic line; and the aff. Diplocynodon from Dormaal (Belgium) and Le Quesnoy (France), nearly contemporaneous of Silveirinha. The Silveirinha Diplocynodon and many other data strongly suggest moist, subtropical, quite limited in space environments related to an alluvial plain crossed by small, meandering channels. Article infos Published in Vol. 32, Fasc. 1 (2003) |
|
|

|
Revision of the family Cephalomyidae (Rodentia, Caviomorpha) and new cephalomyids from the early Miocene of Patagonia.Alejandro KramarzKeywords: Cephalomyidae; Lower Miocene; Patagonia; Rodentia; Soriamys; SystematicsAbstract A new genus of hystricognath rodent with two new species, Soriamys gaimanensis and Soriamys ganganensis, from the Colhuehuapian Age (Early Miocene), Sarmiento Formation, of Patagonia is described. The first species comes from the south barranca of the valley of Rio Chubut, near Gaiman locality (Chubut Province). It is known through a great number of dental remains in different stages of wear. The teeth are protohypsodont, with cement in the principal valleys. P4 are simpler, more oval inoutline and without a differentiated hypocone-hypoflexus. Upper molars are pentalophodont in early stages of wear and become bilobated in middle and advanced stages; M3 have a temporary third posterior lobe due to the maintenance of the braquiflexus on the posterior wall of the tooth. Lower teeth have a completely asymrnetrical pattern in relation to the uppers. The molars are trilophodont, with only one complex crest in the trigonid composed of the fusion of the anterolophid and mesolophid. The dp4 have a derived pentalophodont pattern due to the loss or fusion of the mesolophid and the development of an accessory transverse crest between the anterolophid and metalophid. The second species is known through a complete skull and jaw and other skull fragments with the dentition, proceeding from Pampa de Gan Gan, Chubut province. Respect to the first species, the teeth are higher crowned, with an earlier occlusal simplification and a third posterior lobe of M3 more developed and persistent. The skull and jaws show many chinchilloid characters, such as jugal bone with an ascending process, concave palate, very prominent dorsal shelf of the masseteric fossa, nasolachrymal duct opened laterally on the maxillary and very developed lateral mandibular fossa. Moreover, Soriamys is closely related to Cephalomys by sharing a similar asymmetric dental pattern and other dental and mandibular characters. These two genera constitute a natural group, the Cephalomyidae, with peculiar dental characters, like the asymmetric pattem of the upper and lower teeth; Cephalomyopsis, and probably Litadontomys, can be considered part of this group. Scotamys and Perimys constitute a distinct lineage (the Neopiblemidae or Perimyidae), more closely related to the chinchillids. Many characters shared by cephalomyids, eocardiids and caviids suggest a closer affinity between the Chinchilloidea and the Cavioiidea as a whole. Abrocoma shows also an asymmetric dental pattern and other chinchilloid features that suggest some degree of relationship with the cephalomyids, still not well determined. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 1-2 (2001) |
|
|
|
Description des rongeurs Pliocènes de la faune du Mont-Hélène (Pyrénées-Orientales, France), nouveau jalon entre les faunes de Perpignan (Serrat-d'en-Vacquer) et de Sète.Jean-Pierre Aguilar, Marc Calvet and Jacques MichauxKeywords: Chronology; Climatology; France; Mont-Hélène; Pliocene; RodentsAbstract The Mont-Hélène's fauna [Pyrénées-Orientales, France], includes 15 species of rodents with a new one, Occitanomys montheleni n. sp. among the 9 species of the Murids which are listed. The uncommon Cricetid, Blancomys neglectus, is well represented in the fauna. Peculiarities of the population referred to Slephanomys cf. donnezaniare discussed. The locality a fissure filling may be the oldest one of Tabianian age known in Southern France. The diversity of the Murids gives evidence of a subtropical climate and of a diversified environment which may be linked to the spreading of the coastal plain following the filling up of the Roussillon Neogene Basin. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 3 (1986) |
|
|

|
The new Algerian locality of Bir el Ater 3: validity of Libycosaurus algeriensis (Mammalia, Hippopotamoidea) and the age of the Nementcha FormationFabrice Lihoreau, Lionel Hautier and Mahammed MahboubiKeywords: Dispersal event; Miocene; North Africa; Tetralophodondoi: 10.18563/pv.39.2.e1 Abstract The description of original material of anthracothere and proboscidean in the new locality of Bir el Ater 3 from East Algeria, and a thorough review of early Libycosaurus remains of Bir el Ater 2 allows us validating L. algeriensis as the smallest and earliest species of Libycosaurus and probably the earliest migrant of the genus from Asia. The presence of a Tetralophodon in the Neogene Nementcha formation might represent the earliest occurrence of the genus in Africa. These original fossil remains allow us to discuss the age of the Neogene part of the Nementcha formation close to the Serravalian/Tortonian boundary. Article infos Published in Vol.39-2 (2015) |
|
|
|
Les artiodactyles du gisement yprésien terminal de Premontre (Aisne, France)Jean Sudre and Jorg ErfurtKeywords: Artiodactyls; France; Mammals; new species; YpresianAbstract The artiodactyls (Mammalia) from the latest Ypresian locality of Prémontré from the Paris Basin (niveau repère MP 10 in the lower Eocene of the Paris Basin) are described in this paper. Three species have been identified: 1) Diacodexis cf. varleti SUDRE et al., 1983; 2) a new species of Eurodexis ERFURT & SUDRE (E. russelli nov. sp.) defined after the revision of the species Messelobunodon? ceciliensis from the Lutetian beds of Geiseltal (Germany); and 3) Eurodexeinae indet., a probable ancestor of another form from the Geiseltal which was previously recorded as Homacodon? sp. (Erfurt 1993) and now named Parahexacodus germanicus. The two later forms are referred to the new subfamily Eurodexeinae (Erfurt & Sudre 1996). The analysis of these forms as weIl as comparative studies have led us to reconsider our previous conclusions regarding the content of the species Protodichobune oweni LEMOINE 1878 and some aspects of Ypresian diacodexid evolution. One can postulate that the divergence of E. russelli nov. sp. occurred during the first radiation of these primitive artiodactyls. Some other stem form with bunodont teeth such as Protodichobune and Aumelasia have also differentiated from Diacodexis. Like Eurodexis, these two genera persist during the middle Eocene. The absence of Protodichobune and Aumelasia at Prémontré is probably due to particular ecological conditions. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
A primitive Emballonurid bat (Chiroptera, Mammalia) from the Earliest Eocene of EnglandJerry J. HookerKeywords: bats; Early Eocene; Emballonuridae; Origins; PHYLOGENYAbstract A new genus, Eppsillycteris, is erected for Adapisorex? allglicus COOPER, 1932, from the earliest Eocene Blackheath Beds of Abbey Wood, London, England. Various derived character states indicate that it belongs to the order Chiroptera (bats) rather than to the extinct "insectivore" family Adapisoricidae. Other derived character states are shared with fossil and modern members of the family Emballonuridae. Placement of the new genus in this family extends the record of the Emballonuridae back in time by about 10 million years. It is the earliest record of a modern bat family and one of the earliest bats. This implies that the differentiation of at least some modern bat families took place in the Palaeocene, where no authenticated records of bats yet exist. The primitive characters of the earliest bats make the family Nyctitheriidae an unlikely stem group for the order Chiroptera. A tentative plausible alternative exists in some unnamed upper molars from the Palaeocene of Walbeck, Germany. Wyollycteris chalix, described as a bat from the Late Palaeocene of Wyoming, U,S.A., fits better in the family Nyctitheriidae. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
A new species of hippopotamine (Cetartiodactyla, Hippopotamidae) from the late Miocene Baynunah Formation, Abu Dhabi, United Arab EmiratesJean-Renaud Boisserie, Mathieu Schuster, Mark J. Beech, Andrew Hill and Faysal BibiKeywords: Arab Peninsula; Hippopotamidae; Hippopotamine event; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.41.1.e2 Abstract The discovery of new hippopotamid material from the late Miocene Baynunah Formation (Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates) has prompted the revision of the existing material of this as yet unnamed fossil taxon. The Baynunah hippopotamid appears to be distinct from all other contemporary and later species in having a relatively more elongate symphysis, a feature similar to the earlier (and more primitive) Kenyapotamus. Yet, the Baynunah hippopotamid presents a dentition typical of the Hippopotaminae. It is therefore a distinct species attributed to the later subfamily, described and named in this contribution. This species provides further evidence for a ca. 8 Ma evolutionary event (termed “Hippopotamine Event”) that initiated the spread and ecological significance of the Hippopotaminae into wet habitats across Africa and Eurasia. The morphological affinities of the new species from Abu Dhabi suggest that the Arabian Peninsula was not a dispersal route from Africa toward southern Asia for the Hippopotamidae at ca. 7.5 Ma to 6.5 Ma. Article infos Published in Vol 41-1 (2018) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
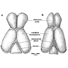
The endocranial cast and encephalization quotient of Ptilodus (Multituberculata, Mammalia)David W. Krause and Zofia Kielan-JaworowskaKeywords: encephaIization quotient; endocranial cast; Montana; Multituberculata; olfactory bulbs; Paleocene; PtilodusAbstract Simpson (1937a) reconstructed the brain of the Paleocene multituberculate Ptilodus as having the olfactory bulbs widest anteriorly, an unusual condition among mammals. Slight preparation and reexamination of the endocast specimens of Ptilodus reveals that the olfactory bulbs in fact taper anteriorly, as in the recently-described endocranial casts of three multituberculate species from the Late Cretaceous of Asia, and as in those of other mammals. The brain of Ptilodus was therefore essentially of the same general pattem as in other multituberculates. Ptilodus differs, however, in having the vermis more deeply inserted between the cerebral hemispheres. Other details concerning the endocast morphology of Ptilodus are clarified. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|
|
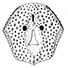
Norselaspis glacialis n.g., n.sp, et les relations phylogénétiques entre les kiaeraspidiens (Osteostraci) du dévonien inférieur du Spitsberg.Philippe JanvierKeywords: Devonian; kiaeraspids; Osteostraci; SpitsbergenAbstract The anatomy of Norselaspis glacialis n.g., n.sp., a primitive kiaeraspidian from the Lower Devonian of Spitsbergen, is described on the basis of spécimens studied by grinding sections or prepared with dilute formic acid. This study yielded some new anatomical details, including the presence of a canal prolonging posteromedially the canal alloted to the facial nerve by Stensiö. This posterior prolongation of the « facial canal ›› into the posterolateral part of the labyrinth cavity is consistent with the hypothesis put forward by Allis, Lindström, Jefferies and Whiting, that this canal housed the glossopharyngeus nerve. Furthermore, in N. glacialis, the foramen usually referred to as the foramen for the œsophagus opens posteriorly into a cavity in the postbranchial wall, referred to here as the intramural cavity, and which is interpreted as having housed the heart. Consequently, the œsophagus probably accompanied the dorsal aorta through the aortic canal. Finally, the foramen generally interpreted as having transmitted the ventral afferent arterial trunk is here considered as having housed the hepatic vein, which emptied into the venous sinus of the heart. The ventral afferent arterial trunk may thus have passed through the former «œsophageal ›› foramen. Article infos Published in Vol. 11, Fasc. 2-3 (1981) |
|
|
|
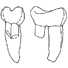
The Gliridae (Mammalia) from the oligocene (MP24) of Gröben 3 in the folded molasse of southern GermanyUndine UhligKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Cyrena Beds; folded molasse; Germany; Gliridae; level MP 24; Mammals; Oligocene; PalaeoecologyAbstract This study describes four taxa of Gliridae from the Oligocene mammal locality Gröben 3: Gliravus tenuis BAI-ILO, 1975, Bransatoglis micio (MISONNE, 1957), B. planus (BAHLO, 1975) and B. heissigi n. sp. Gliravus tenuis from Gröben 3 is somewhat more advanced than the type population found in Heimersheim. This confirms previous research suggesting that Gröben 3 should be dated earlier than Heimersheim (MP 24). The first documented occurrence of B. mício around level MP 24 was found in Gröben 3. An abundance of tooth material from B. planus in Gröben 3 makes it possible, for the first time, to observe evolutionary stages within this species from MP 21 until MP 28. B. heissigi n. sp. is restricted to level MP 24. This species is located between B. mísonnei (MP 20 - 23) and Microdyromys praemurinus (MP 25 - 28). Within the lineage Bransatoglis bahloi - B. misonnei - B. heissigi, a decrease in size is noticeable. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 3-4 (2001) |
|
|
|
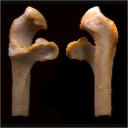
New remains of the very small cuckoo, Chambicuculus pusillus (Aves, Cuculiformes, Cuculidae) from the late Early/early Middle Eocene of Djebel Chambi, TunisiaCécile Mourer-Chauviré, El M. Essid, Hayet Khayati Ammar, Laurent Marivaux, Wissem Marzougui, Rim Temani, Monique Vianey-Liaud and Rodolphe TabuceKeywords: Cuckoos; Eocene; Fossil birddoi: 10.18563/pv.40.1.e2 Abstract Abstract: A very tiny cuckoo, Chambicuculus pusillus, was recently described after a few fragments of tarsometatarsi from the late Early/early Middle Eocene of Djebel Chambi, Tunisia. New remains, notably a coracoid, confirm the attribution of this genus to the recent family Cuculidae. This coracoid shows a very elongate and strap-like processus procoracoideus. This morphological feature is otherwise only known in the family Cuculidae. The characteristics of the coracoid and tarsometatarsi show that Chambicuculus is morphologically more advanced over the other stem cuculids described in Europe and North America. Chambicuculus is the oldest Cuculidae known so far. Article infos Published in Vol.40-1 (2016) |
|
|
|
Systematic revision of Ctenodactylidae (Mammalia, Rodentia) from theMiocene of Pakistan.J.A. BaskinKeywords: Ctenodactylidae; Miocene; Prosayimys; Rodents; Sayimys; SiwalikAbstract Extensive sampling of the Siwalik deposits of the Potwar Plateau of northem Pakistan and from the Zinda Pir dome of central Pakistan has produced a fossil record of Miocene ctenodactylids that can be correlated with the paleomagnetic time scale. The early Miocene Prosayimys flynni (n. gen., n. sp.) is recognized as the first ctenodactylid in the Indian subcontinent. Prosayimys is ancestral to Sayimys. From the late early Miocene to the early late Miocene, there is an anagenetic succession of three species of Sayimys: S. cf. S. intermedius, S. sivalensis, and S. chinjiensis (n. sp.). Sayimys chinjiensis gave rise to the late late Miocene S. perplexus. A second lineage is represented by Sayimys minor, S. sp. A, and S. sp. B. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 1 (1996) |
|
|

|
First evidence of an early Miocene marine teleostean fish fauna (otoliths) from la Paillade.(Montpellier,France)Bettina Reichenbacher and Henri CappettaKeywords: Aquitanian; Biostratigraphy; La Paillade; marine deposits; Miocene; otoliths; Palaeoecology; Palaeogeography; Southern France; TeleosteiAbstract A fossil fish fauna, based on 5533 otoliths, from the La Paillade locality at Montpellier is described and figured. The otolith-bearing marls correlate to mammal zone MN l (Aguilar, 1982), and thus represent the earliest Miocene. The fish fauna consists of 30 taxa belonging to 20 families. Two species are new: Dussumieria sittigi and Liza gaudanti. The predominant faunal element is the Lesueurigobius vicínalis-species complex, composing 73% of all investigated otoliths. The palaeoecological analysis reveals a marine to euryhaline fish fauna living under tropical to subtropical conditions in the transition zone littoral - sublittoral. Water depth probably was more than 10 m. The scarcity of pelagic físhes suggests that the habitat was either a sheltered bay and/or far away from the open sea. Furthermore, some genera represented in the La Paillade fish fauna presently live exclusively in the Indopacific realm. Their presence strongly supports a broad connection between the Indian Ocean, the Mediterranean, and the Paratethys Seas during the Early Miocene (Aquitanian). From a palaeobiogeographical point of view, faunal relationships were found between the La Paillade fish fauna and both the Paratethys fish fauna and the fish fauna from the deposits in the Upper Rhinegraben and the Mayence and Hanau Basins (Germany). Article infos Published in Vol. 28, Fasc. 1 (1999) |
|