Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
New Paleocene chimaeroid from Maryland
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
Modification du statut générique de quelques espèces de sélaciens crétacés et tertiairesHenri CappettaKeywords: Cretaceous; Selachians; TertiaryAbstract The re-examination of six fossil selachian species has involved the creation of six new genera: Squatiscyllium, Protolamna, Parotodus, Abdounia, Physogaleus, Hypolophodon and of one new species : Prozolamna sokolovi. The modification of the generic statute of these species allows to clarify their systematic position and to define their relationships at a familial level. Article infos Published in Vol. 10, Fasc. 1 (1980) |
|
|
|
Les Palaeotheridae (Perissodactyla) de la faune de Mammifères de Fons 1 (Eocène supérieur).Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Anchilophus; Eocene; Pachynolophus; Palaeotheriidae; Perissodactyladoi: 10.18563/pv.1.1.1-46 Abstract The locality of Fons 1, one of the fossiliferous outcrops in the late Eocene limestones of Fons-outre-Gardon (Gard), has yielded varied remains of mammals. The specimens were prepared by dilute acetic acid attack on the rock and by impregnation with an acrylic resin. Article infos Published in Vol. 01, Fasc. 1 (1967) |
|
|

|
The Pleistocene vertebrate fauna of Robinson Cave, Overton County, TennesseeJ. E. Guilday, H. W. Hamilton and A. D. Mc CradyKeywords: Fauna; Mammalia; Pleistocene; Tennesseedoi: 10.18563/pv.2.2.25-75 Abstract A late Pleistocene deposit of 60 species of vertebrates and 12 of invertebrates is described from Robinson Cave, Overton County, Tennessee, U.S.A. Forty-eight species of mammals are represented by at least 2,483 individuals; 10 % are extinct, 10 % occur in the state only as boreal relicts in the Great Smoky Mountains; 23 % no longer occur as far south as Tennessee; 57 % occur at or near the site today. Nínety-one percent of the Recent mammal species can be found living today in the Minnesota-Wisconsin area, approximately 10 degrees farther north. Fluorine analysis suggests a long period of accumulation. The following 10 mammalian species are recorded from Tennessee for the first time. Sorex arcticus, Microsorex hoyi, Citellus tridecemlineatus, Clethrionomys gapperi, Microtus pennsylvanicus, Synaptomys cooperi, Synaptomys borealis, Zapus nudsonius, Napaeozapus insignis, Martes americana. Six additional species are present as boreal relicts in the Great Smoky Mountains of eastern Tennessee but not at the site today : Sorex cinereus, Sorex dispar, Sorex palustris, Parascalops breweri, Glaucomys sabrinus, Mustela nivalis. Six forms are extinct: Canis dirus, Ursus americanus amplidens, Sangamona furtiva, Dasypus bellus, Mammut americanus,Megalonyx jeffersoni. Twenty-six additional species of mammals, all of the snails, birds, reptiles, and amphibians recovered from the fauna still inhabit the area today: The fauna is indicative of a cold-temperate climatic episode associated with the Wisconsin glaciation, but may be chronologically mixed. Article infos Published in Vol. 02, Fasc. 2 (1969) |
|
|

|
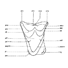
Evolution of the Rhizomyine zygomaLawrence J. Flynn, Mohammed Sarwar and Jean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: parallel evolution; Rhizomyidae; Rodentia; Siwalik; zygomaAbstract Cranial anatomy of a late Miocene rhizomyid, Brafhyrhizomys cf. B. pilgrimi, provides new evidence on the origin of the dorsal, round infraorbital foramen of living rhizomyines. Primitive rhizomyids retain a myomorphous keyhole foramen with a long ventral slit that retracts upward during the evolutionary history of the Rhizomyidae. The primitive condition of the elongated ventral slit is represented by Kanisamys sivalensis. Among later burrowers the foramen shows progressive dorsal migration, the ventral slit terminating midway up the snout in B.tertracharax and B. choristos ; well above the midline of the snout in Brachyrhizamys cf. B. pilgrimi. Apparently this transformation began earlier among Rhizomyinae than among Tachyoryctinae and continued to a more derived stage in rhizomyines. ln living Rhizomyx the ventral slit is absent and only a high round hole remains at the anterior end of the zygomatic arch. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 3 (1985) |
|
|

|
Paleobiology of Messel ErinaceomorphsGerhard StorchKeywords: Erinaceomorpha; Germany; Grube Messel; Lipotyphla; Middle Eocene; PaleobiologyAbstract Three erinaceomorph species are known from the early Middle Eocene of Grube Messel near Darmstadt, Germany, which are referred to the family Amphilemuridae. Pholidocercus hassiacus, Macrocranion tupaiodon, and Macrocranion tenerum showed extraordinary adaptations to their different life strategies, and several of their specializations are unknown among living insectivores. Pholídocercus was a well-defended robust animal with an opportunistic feeding strategy. Macrocraníon zupaiodon was a slender forest floor-dweller with saltatorial specializations to escape from predators; fishes were the preferred component of its omnivorous diet. Macrocranion tenerum exhibited a combination of both survival strategies, extremely elongated hind limbs for rapid and even ricochetal flight and a spiny exterior as an effective protective device; it was probably specialized for feeding on ants. Thus, closely related, omnivorous-insectivorous forest floor-dwellers could exploit the Messel ecosystem. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
|
Révision systématique des Anchilophini (Palaeotheriidae, Perissodactyla, Mammalia).Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Anchilophus; Eocene; new genus; new species; Palaeotheriidae; Paranchilophus; Perissodactyla; Systematicsdoi: 10.18563/pv.37.1-3.1-165 Abstract The knowledge of the Anchilophini has been lately renewed by the discovery of a rather large amount of new material still largely unpublished. This new material offers the opportunity of a systematic revision of this tribe gathering those of European Eocene Equoidea which bear no mesostyle on upper check teeth and display a heavy trend to the molarization of premolars. Article infos Published in Vol. 37, Fasc. 1-3 (2012) |
|
|

|
Lissamphibians from Dams (Quercy, SW France): Taxonomic identification and evolution across the Eocene-Oligocene transitionAlfred Lemierre and Maeva J. OrliacKeywords: Eocene-Oligocene; Grande Coupure; Lissamphibia; Quercy Phosphoritesdoi: 10.18563/pv.48.1.e3 Abstract The locality of Dams (Quercy, southwestern France) has yielded two fossil assemblages, one from the late Eocene and another from the early Oligocene, making it one of the few localities with infillings across the Eocene-Oligocene transition. At least 24 taxa (13 mammals, 11 snakes) have been identified in this locality. Study of the lissamphibian remains from Dams yields an Eocene and an Oligocene assemblage, with a total of eight taxa. The Eocene assemblage includes two unnamed salamandrine species, one unnamed pelobatid species and one pyxicephalid species (Thaumastosaurus). The Oligocene assemblage includes two unnamed pleurodeline species, one salamandrine species (Salamandra sansaniensis) and an unnamed pelobatid species. Among the eight taxa from Dams, one Eocene salamandrine and one Oligocene pleurodeline are identified for the first time in the Quercy. A review of the lissamphibians from the Quercy area identifies eleven taxa for the Late Eocene (MP19) and eight taxa for Early Oligocene (MP22), with a major turnover at the Eocene-Oligocene transition. This turnover occurs in a time of major climatic changes, with a significant decrease in temperature and precipitation and concurrent increase in seasonality in Europe, likely affecting specialized taxa. Article infos in press |
|
|
|
Contribution à l'étude des Cricétidés oligocènes d'Europe occidentaleMonique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: Cricetidae; Europe; Oligocenedoi: 10.18563/pv.5.1.1-44 Abstract Of the ten cricetid species from the Oligocene of Western Europe, attributed until now to the genus Eucricetodon, only four prove to be utilizable - E. atavus, E. huberi, E. praecursor, E. collatum - to which it is possible to add two forms newly described: E. huerzeleri and E. quercyi. The evolullon of the genus Pseudocricetodon is also the subject of new observations. The study of the dental morphology allows us to distinguish in these two genera three lineages beginning in the middle Oligocene: Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 1 (1972) |
|
|
|
Mammals and stratigraphy : Geochronology of the continental mammal-bearing Tertiary of south America.Larry G. Marshall, Robert Hoffstetter and Rosendo PascualKeywords: Cenozoic; Geochronology; Mammalia; South America; Stratigraphy; TertiaryAbstract The principles and practices employed in establishment and recognition of South American land mammal ages are reviewed along with previous and present concepts of distinguishing time, rock, and faunal units. Previous chronological arrangements of South American Tertiary land mammal faunas are appraised on the basis of recent geological and paleontological data. Twelve South American Tertiary land mammal ages are here recognized [from oldest to youngest, Riochican (middle to late Paleocene); Casamayoran (early Eocene); Mustersan (middle Eocene); Divisaderan (late Eocene); Deseadan (early [to middle?] Oligocene); Colhuehuapian (late Oligocene); Santacrucian (early Miocene); Friasan (middle Miocene); Chasicoan (late Miocene); Huayquerian (latest Miocene); Montehermosan (early to middle Pliocene); and Chapadmalalan (late Pliocene)]. As all except the Friasian were originally defined on the basis of Argentine faunas, these are discussed first and at length, and each is reviewed with discussion of type locality, stratigraphy, type fauna, and faunal correlations. Non-Argentine faunas are then discussed country by country in alphabetical order. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Ext (1983) |
|
|
|
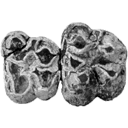
A new study of the anthracotheres (Mammalia, Artiodactyla) from pondaung formation, Myanmar: systematics implicationsAung N. SoeKeywords: Anthracohyus; Anthracokeryx; Anthracotherium; Pondaung Formation; sexual dimorphism; Siamotherium; South East Asia; taxonomydoi: 10.18563/pv.36.1-4.89-157 Abstract Anthracotheres from the Pondaung Formation, Myanmar, are considered as one of the most primitive artiodactyl groups and they represent the oldest known record in the world. Thus, the understanding of this group has numerous implications for evolutionary biology and biochronological correlations. However, the systematlcs of these mammals has been interpreted in different ways, and the main debate focuses on the number of taxa represented in the Pondaung Formation. The revised taxonomy proposed here is mainly based on the relative development of the upper molar W-shaped ectoloph, system of crests and stylar cusps, and on body size. On the basis of these characters, they are classified into four genera including six different species. Two well-known genera, Anthracotherium and Anthracokeryx, are validated and more precisely diagnosed. Anthracokeryx possesses a better developed W-shaped ectoloph, system of crests and stylar cusps than Anthracotherium, which displays notable differences with the more derived representatives of this genus. Both of these Pondaung genera show evidence for sexual dimorphism. However, the incompleteness of fossil material fueled a debate concerning the status of two additional Pondaung anthracotheres, Siamotherium and Anthracohyus. The latter genus is of uncertain affinities, but it has been considered as a hippopotamid ancestor. Despite new material attributed to these two forms, additional discoveries are still required to establish their taxonomic status. The hypothesis that Southeast Asia was the centre of origin of Anthracotheriidae is supported by the retention of numerous primitive dental characters in these taxa and by the antiquity of the Pondaung Formation, to which an age of 37 My is now generally accepted. Article infos Published in Vol. 36, Fasc. 1-4 (2008) |
|
|
|
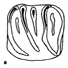
Les insectivores des phosphorites du QuercyJean-Yves CrochetKeywords: Insectivores; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Many types of insectivores have been described from specimens found in the Quercy phosphorites. These remains very often were not dated because they came from old collections. Recent excavations have permitted the situation of Amphidozotherium cayluxi FILHOL in the late Eocene. Two new genera are descrlbed based on material both from the old collections (Cryplotopos nov. g.) and from that recently recovered (Darbonetus nov. g., beginning of the middle Oligocene). Their systematic positions are revised and comparisons with American faunas are made. Amphidozotherium is not a talpid, but an erinaceoid belonging to an indeterminate family. Saturninia gracilis STHELIN is classified among the Nyctitheriinae, Myxomygale antiqua FILHOL among the Urotrichini Talpinae, and the genus Geotypus POMEL among the Scaptonichini Talpinae. A new study of the talpids from Auvergne has been rendered necessary. During the late Eocene and Oligocene precise morphology relationships existed between certain insectivores of Europe and North America. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|

|
An Australian Miocene Brachipposideros (Mammalia, Chiroptera) related to Miocene representatives from FranceBernard Sigé, Suzanne J. Hand and Michael ArcherKeywords: Australia; bats; Chiroptera; MioceneAbstract A new middle Miocene hipposiderid bat is described from a limestone deposit on Riversleigh Station in north-western Queensland. Hipposideros (Brachipposideros) nooraleebus n. sp. is the first record of this subgenus from anywhere in the world outside of France. The palaeoecological setting of the fossil bats appears to have been a relatively quiet, sunny lime-enriched tropical pool that contained tortoises, crocodiles and fish. It is possible that the bats were washed into the pool from an adjacent cave. Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 5 (1982) |
|
|

|
Les poissons crétacés et tertiaires du bassin des Iullemmeden (République du Niger)Henri CappettaKeywords: Actinopterygians; Cenozoic; Cretaceous; Dipnoans; SelachiansAbstract The present work is devoted to the study of the Cretaceous and Tertiary fishes (teeth of Selachians, Actinopterygians and Dipnoans) collected during a recent expedition in Niger. The Maestrichtian localities have yielded a new genus and a new subspecies of Selachian: Igdabatis sigmodon nov. gen., nov. sp. and Lamna biauriculata nigeriana nov. subsp. The locality of Sessao, which has been attributed to the Thanetian by means of the study of the fish, has furnished by screen-washing an interesting fauna wherein six new species are described: Raja Iouisi, Dasyatis sessaoensis, D. sudrei, D. russelli, Hypolophites thaleri and Ceratodus casieri. Comparison of these faunas with contemporary faunas of Africa has brought out a certain endemism in the Iullemmeden Basin during the late Cretaceous and the early Tertiary. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 5 (1972) |
|
|
|
Description des rongeurs Pliocènes de la faune du Mont-Hélène (Pyrénées-Orientales, France), nouveau jalon entre les faunes de Perpignan (Serrat-d'en-Vacquer) et de Sète.Jean-Pierre Aguilar, Marc Calvet and Jacques MichauxKeywords: Chronology; Climatology; France; Mont-Hélène; Pliocene; RodentsAbstract The Mont-Hélène's fauna [Pyrénées-Orientales, France], includes 15 species of rodents with a new one, Occitanomys montheleni n. sp. among the 9 species of the Murids which are listed. The uncommon Cricetid, Blancomys neglectus, is well represented in the fauna. Peculiarities of the population referred to Slephanomys cf. donnezaniare discussed. The locality a fissure filling may be the oldest one of Tabianian age known in Southern France. The diversity of the Murids gives evidence of a subtropical climate and of a diversified environment which may be linked to the spreading of the coastal plain following the filling up of the Roussillon Neogene Basin. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 3 (1986) |
|
|
|
Reflections on some Russian eotheriodonts (Reptilia, Synapsida, Therapsida)Denise Sigogneau-Russell and P. K. TchudinovKeywords: Reptilia; Russia; Synapsida; Therapsidadoi: 10.18563/pv.5.3.79-109 Abstract As a result of the enrichment of eotheriodont material by one of us (P.K.T.), these specimens (essentially Biarmosuchur and Eotitanosuchur) are reexamined and refigured. A reevaluation of their particularities supports the distinction of two families, for which new diagnoses are proposed. This leads us to discuss the affinities of these families, with respect to the sphenacodonts on one hand, and to the South African primitive theriodonts on the other (gorgonopsids and ictidorhinids). This study contains inherent paleogeographic consequences which are considered in conclusion. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 3 (1972) |
|
|
|
Les Issiodoromyinae (Rodentia, Theridomyidae) de l'Eocène supérieur à l'Oligocène supérieur en Europe occidentaleMonique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: climate; Faunal turnover; PaléogèneAbstract Based on material from 30 localities, morphologic dental, cranial and biometric analyses have permitted the characterization of two parallel Issiodoromyine lineages, and also the definition of diverse species representing several evolutive stages. Thus it is that new lineages complete the contribution made by the Theridomyinae and Cricetidae and permit, for the Quercy in particular, additional precision in the biochronologic succession of the localities. One of the lineages is limited to the genus Pseudoltinomys LAVOCAT; the other evolves from the genus Elfomys HARTENBERGER to the genus Issiodoromys BRAVARD in GERVAIS. The latter is affected by profound anatomical changes due to a functional modification of the mastication apparatus. These changes seem to be able to be put in relation with the aridification and cooling of the climate at the end of the Eocene. At the end of the middle Oligocene, a new chewing structure is achieved. It is found in diverse living rodents that inhabit a rather arid steppe environment (Cavia, Pedetes, Ctenodactylus). To these supposed nearby ecologic conditions, these rodents have responded in a convergent fashion. It is possible to attribute to the extreme specialization of Issiodoromys its incapacity to adapt to the new climatic crisis of the end of the Oligocene. The arrival of immigrants may be considered as another cause of its disappearance at this time, complementary or not with the first. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 1-2 (1976) |
|
|

|
Contribution à la classification des pistes de vertébrés du Trias: Les types du Stormberg d'Afrique du Sud (1).Paul EllenbergerKeywords: Footprints; South Africa; Stormberg; TriasAbstract No abstract available Article infos Published in Vol. 5, Ext (1972) |
|
|
|
The Gliridae (Mammalia) from the oligocene (MP24) of Gröben 3 in the folded molasse of southern GermanyUndine UhligKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Cyrena Beds; folded molasse; Germany; Gliridae; level MP 24; Mammals; Oligocene; PalaeoecologyAbstract This study describes four taxa of Gliridae from the Oligocene mammal locality Gröben 3: Gliravus tenuis BAI-ILO, 1975, Bransatoglis micio (MISONNE, 1957), B. planus (BAHLO, 1975) and B. heissigi n. sp. Gliravus tenuis from Gröben 3 is somewhat more advanced than the type population found in Heimersheim. This confirms previous research suggesting that Gröben 3 should be dated earlier than Heimersheim (MP 24). The first documented occurrence of B. mício around level MP 24 was found in Gröben 3. An abundance of tooth material from B. planus in Gröben 3 makes it possible, for the first time, to observe evolutionary stages within this species from MP 21 until MP 28. B. heissigi n. sp. is restricted to level MP 24. This species is located between B. mísonnei (MP 20 - 23) and Microdyromys praemurinus (MP 25 - 28). Within the lineage Bransatoglis bahloi - B. misonnei - B. heissigi, a decrease in size is noticeable. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 3-4 (2001) |
|
|

|
Saturnin Garimond (1914-1987)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: biographyAbstract Biographie et liste des publications de S. Garimond. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 3 (1987) |
|
|
|
Les artiodactyles du gisement yprésien terminal de Premontre (Aisne, France)Jean Sudre and Jorg ErfurtKeywords: Artiodactyls; France; Mammals; new species; YpresianAbstract The artiodactyls (Mammalia) from the latest Ypresian locality of Prémontré from the Paris Basin (niveau repère MP 10 in the lower Eocene of the Paris Basin) are described in this paper. Three species have been identified: 1) Diacodexis cf. varleti SUDRE et al., 1983; 2) a new species of Eurodexis ERFURT & SUDRE (E. russelli nov. sp.) defined after the revision of the species Messelobunodon? ceciliensis from the Lutetian beds of Geiseltal (Germany); and 3) Eurodexeinae indet., a probable ancestor of another form from the Geiseltal which was previously recorded as Homacodon? sp. (Erfurt 1993) and now named Parahexacodus germanicus. The two later forms are referred to the new subfamily Eurodexeinae (Erfurt & Sudre 1996). The analysis of these forms as weIl as comparative studies have led us to reconsider our previous conclusions regarding the content of the species Protodichobune oweni LEMOINE 1878 and some aspects of Ypresian diacodexid evolution. One can postulate that the divergence of E. russelli nov. sp. occurred during the first radiation of these primitive artiodactyls. Some other stem form with bunodont teeth such as Protodichobune and Aumelasia have also differentiated from Diacodexis. Like Eurodexis, these two genera persist during the middle Eocene. The absence of Protodichobune and Aumelasia at Prémontré is probably due to particular ecological conditions. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|