Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Abstract book of the 18th Conference of the EAVP
Two enigmatic rodents from Lavergne (MP 16), Quercy Phosphorites
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)
|
Les Issiodoromyinae (Rodentia, Theridomyidae) de l'Eocène supérieur à l'Oligocène supérieur en Europe occidentaleMonique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: climate; Faunal turnover; PaléogèneAbstract Based on material from 30 localities, morphologic dental, cranial and biometric analyses have permitted the characterization of two parallel Issiodoromyine lineages, and also the definition of diverse species representing several evolutive stages. Thus it is that new lineages complete the contribution made by the Theridomyinae and Cricetidae and permit, for the Quercy in particular, additional precision in the biochronologic succession of the localities. One of the lineages is limited to the genus Pseudoltinomys LAVOCAT; the other evolves from the genus Elfomys HARTENBERGER to the genus Issiodoromys BRAVARD in GERVAIS. The latter is affected by profound anatomical changes due to a functional modification of the mastication apparatus. These changes seem to be able to be put in relation with the aridification and cooling of the climate at the end of the Eocene. At the end of the middle Oligocene, a new chewing structure is achieved. It is found in diverse living rodents that inhabit a rather arid steppe environment (Cavia, Pedetes, Ctenodactylus). To these supposed nearby ecologic conditions, these rodents have responded in a convergent fashion. It is possible to attribute to the extreme specialization of Issiodoromys its incapacity to adapt to the new climatic crisis of the end of the Oligocene. The arrival of immigrants may be considered as another cause of its disappearance at this time, complementary or not with the first. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 1-2 (1976) |
|
|

|
The stratigraphic sequence of North American rodent faunasRobert W. WilsonKeywords: North America; Rodents; Stratigraphic sequenceAbstract Rodents first appear in the latest Paleocene or earliest Eocene as very fragmentary specimens (Family Paramyidae) known largely from a single locality. After this sparse beginning, rodents are usually abundant in the North American record if proper recovery methods are used. Utilization of rodents for biostratigraphic purposes depends on 1/ extinction, and 2/ replacement by evolution of endemic groups and/or incursions of Old World rodents, and rarely and late by South American kinds. These incursions are separated by relatively long periods of isolation in the Paleogene, but more episodic in the Neogene. At least 10 rodent zones can be characterized by major distinctions, and these zones can be amplified into as many as 16 with little trouble. In general, rodent genera permit as refined a zonation as do genera of large mammals. Distinction at a specific level has not been attempted herein except in the Blancan and Post-Blancan. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Saturnin Garimond (1914-1987)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: biographyAbstract Biographie et liste des publications de S. Garimond. Article infos Published in Vol. 17, Fasc. 3 (1987) |
|
|

|
Designating a lectotype for Mesacanthus pusillus (Gnathostomata: Acanthodii)Matthew Baron and Kevin SeymourKeywords: acanthodians; Chordata; Devonian; Midland Valley; Orcadian Basindoi: 10.18563/pv.44.1.e2 Abstract The early gnathostome genus Mesacanthus is well represented in both Lower Old Red Sandstone and Middle Old Red Sandstone assemblages of northern and central Scotland. This ‘acanthodian’ taxon is currently thought to comprise two valid species: M. mitchelli and M. pusillus. Although the whereabouts of the holotype of M. mitchelli (NHMUK PV P560) is known, the syntype material for M. pusillus has long been thought lost. Here we identify at least one specimen that formed part of the original syntype material for M. pusillus, albeit in a slightly different condition than when it was originally figured. This specimen is ROM 25872, which is here designated as the lectotype. A second specimen – ELGNM 1978.191.1 – could represent another of the syntype specimens, but poor preservation quality makes it impossible to be certain. Article infos Published in 44-1 (2021) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
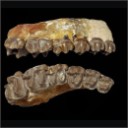
Reflections on some Russian eotheriodonts (Reptilia, Synapsida, Therapsida)Denise Sigogneau-Russell and P. K. TchudinovKeywords: Reptilia; Russia; Synapsida; Therapsidadoi: 10.18563/pv.5.3.79-109 Abstract As a result of the enrichment of eotheriodont material by one of us (P.K.T.), these specimens (essentially Biarmosuchur and Eotitanosuchur) are reexamined and refigured. A reevaluation of their particularities supports the distinction of two families, for which new diagnoses are proposed. This leads us to discuss the affinities of these families, with respect to the sphenacodonts on one hand, and to the South African primitive theriodonts on the other (gorgonopsids and ictidorhinids). This study contains inherent paleogeographic consequences which are considered in conclusion. Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 3 (1972) |
|
|
|
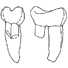
Les Périssodactyles (Mammalia) du gisement Bartonien supérieur de Robiac (Éocène moyen du Gard, Sud de la France)Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Chasmotherium; new species; Palaeotheriidae; paleoenvironmentsdoi: 10.18563/pv.39.1.e3 Abstract We present here a new updated counting of the perissodactyls of Robiac, the type locality of the MP 16 level of the biochronological scale of paleogene mammals and that of the Robiacian stage of Eocene Land Mammals Ages in Western Europe. Article infos Published in Vol.39-1 (2015) |
|
|

|
Rongeurs (Mammalia, Rodentia) du Miocène de Beni-MellalJean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Morocco; NeogeneAbstract The rodent fauna of Beni-Mellal is characterized by the abundance of ctenodactylids and cricetids. The latter are represented by four distinct species, among which a new form. Dakkamys zaiani nov. gen., nov. sp. is described. A detailed morphological analysis shows that, contrary to that which had been established before, « Cricetodon ›› atlasi Lavocat, 1961, is not closely related to any European form known; this species is attributed, in consequence, to the new genus Mellalomys. A simple biometric analysis has shown that the genus Myocricetodon Lavocat, 1952, is represented in this locality by two distinct species. The systematic homogeneity of the Beni-Mellal cricetids is also demonstrated: they can, as a matter of fact, all be referred to the subfamily Myocricetodontinae. The definition of this subfamily is completed. The sciurids and glirids are also reviewed in the light of new systematic and biogeographic information established ln Europe. A new species of Atlantoxevus from the early Pleistocene of Morocco, A. huvelini nov. sp., is described. It is probably the descendant of A. tadlae from Beni-Mellal. Biogeographic analysis leads one to consider this fauna as the result of geographic isolation in the Maghreb since the late Oligocene or the early Miocene. In particular no direct European influence can be discerned. Stratigraphic considerations resulting from the discovery of new localities in North Africa lead to the confirmation of the ante-Vallesian age of this fauna and to its parallelism with the faunas of La Grive in Western Europe and Fort Ternan in East Africa. The peculiar geologic nature of this locality is discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 4 (1977) |
|
|
|
The Gliridae (Mammalia) from the oligocene (MP24) of Gröben 3 in the folded molasse of southern GermanyUndine UhligKeywords: Biostratigraphy; Cyrena Beds; folded molasse; Germany; Gliridae; level MP 24; Mammals; Oligocene; PalaeoecologyAbstract This study describes four taxa of Gliridae from the Oligocene mammal locality Gröben 3: Gliravus tenuis BAI-ILO, 1975, Bransatoglis micio (MISONNE, 1957), B. planus (BAHLO, 1975) and B. heissigi n. sp. Gliravus tenuis from Gröben 3 is somewhat more advanced than the type population found in Heimersheim. This confirms previous research suggesting that Gröben 3 should be dated earlier than Heimersheim (MP 24). The first documented occurrence of B. mício around level MP 24 was found in Gröben 3. An abundance of tooth material from B. planus in Gröben 3 makes it possible, for the first time, to observe evolutionary stages within this species from MP 21 until MP 28. B. heissigi n. sp. is restricted to level MP 24. This species is located between B. mísonnei (MP 20 - 23) and Microdyromys praemurinus (MP 25 - 28). Within the lineage Bransatoglis bahloi - B. misonnei - B. heissigi, a decrease in size is noticeable. Article infos Published in Vol. 30, Fasc. 3-4 (2001) |
|
|
|
Contributions à l'étude du gisement Miocène supérieur de Montredon (Hérault). Les grands mammifères. 5 - Les périssodactyles EquidaeVéra EisenmannKeywords: Equidae; Hipparion; Late Vallesian; Mammalia; Montredon; PerissodactylaAbstract Revision of the hipparion material from Montredon, including newly excavated and other unpublished specimens brings evidence of specific heterogeneity. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Ext (1988) |
|
|
|
Cricetid rodents from Siwalik deposits near Chinji village. Part I: Megacricetodontinae, Myocricetodontinae and Dendromurinae.Everett H. LindsayKeywords: Dendromurinae; Megacricetodontinae; Middle Miocene; Myocricetodontinae; Rodents; SiwalikAbstract Seventeen species of cricetid rodent are recognized and described from lower and middle Siwalik deposits in the Potwar Plateau of Pakistan. These species are grouped in three categories, characterized as subfamilies (e. g., Megacricetodontinae, Myocricetodontinae, and Dendromurinae); an additional and more abundant category of rodents from these deposits, the Democricetodontinae, is excluded from this study, and will be described in a later study. Fifteen of the species are new, and four new genera are described. The Siwalik cricetid taxa are : Megacricetodon aquilari, n. sp.; Megacricetodon sivalensis, n. sp.; Megacricetodon daamsi, n. sp.; Megacricetodon mythikos, n. sp.; Punjabemys downsi, n. gen. & n. sp.; Punjabemys leptos, n. gen. & n. sp.; Punjabemys mikros, n. gen. & n. sp.; Myocricetodon sivalensis, n. sp.; Myocricetodon sp.; Dakkamyoides lavocati, n. gen. & n. sp.; Dakkamyoides perplexus, n. gen. & n. sp.; Dakkamys asiaticus, n. sp.; Dakkamys barryi, n. sp.; Dakkamys sp.; Paradakkamys chinjiensis, n. gen. & n. sp.; Potwarmus primitivus, n. gen.; and Potwarmus minimus, n. gen. & n. sp. This diverse record of middle Miocene small mammals illuminates a profound radiation of cricetid rodents in southem Asia, the effects of which were felt in Europe and Africa as well as the rest of Asia. Article infos Published in Vol. 18, Fasc. 2 (1988) |
|
|
|
Autopsie d’une radiation adaptative : Phylogénie des Theridomorpha, rongeurs endémiques du Paléogène d’Europe - histoire, dynamique évolutive et intérêt biochronologiqueMonique Vianey-Liaud and Laurent MarivauxKeywords: Diversification; Extinction; Paléoenvironnements; Rodentia; Theridomyoideadoi: 10.18563/pv.40.3.e1 Abstract Résumé : Article infos Published in Vol 40-3 (2016) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
Contribution à l'étude des genres Gliravus et Microparamys (Rodentia) de l'Eocène d'Europe.Jean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Eocene; Gliravus; Microparamys; Rodentiadoi: 10.18563/pv.4.4.97-135 Abstract Based on material found in about 15 localities the relationships of the genera Microparamys and Glirarus have been studied. One new genus, two subgenera and three species [Microparamys (Sparnacomys) chandoni n. subgen. and n. sp., Microparamys (Pantrogna) russelli n. subgen., Eoglirarus wildi n. gen. and n. sp., Gliravus meridionalis n. sp.] as well as the publication Article infos Published in Vol. 04, Fasc. 4 (1971) |
|
|

|
Strange Eocene rodents from SpainPablo Pelaez-Campomanes and Nieves Lopez-MartinezKeywords: Biogeography; Eocene; PHYLOGENY; Rodents; Spain; Zamoramys extraneus n. gen. n. sp.Abstract A new European rodent from the middle Eocene of Spain, Zamoramys extraneus n. gen., n. sp., appears to be closely related to the middle Eocene chapattimyid rodents of Indo-Pakistan. This contradicts the generally accepted paleobiogeographic hypothesis of a Tethyian barrier between Europe and Asia isolating Europe during the middle Eocene. Because of this barrier, some authors have proposed that European and Asian rodents were not closely related, their similarity being the result of morphological convergence. Here monophyly has been tested, using the parsimony criterion, based on an analysis of dental characters (including discussing of homology and the validity of some characteristics). Our results indicate a phylogenetic relationship among the Asiatic Ctenodactyloidea, Zamoramys from Spain, and the European endemic Theridomyoidea. We also conclude from our analysis that theridomyoids and European ischyromyoids are probably not closely related phylogenetically. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|
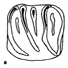
|
Description des rongeurs Pliocènes de la faune du Mont-Hélène (Pyrénées-Orientales, France), nouveau jalon entre les faunes de Perpignan (Serrat-d'en-Vacquer) et de Sète.Jean-Pierre Aguilar, Marc Calvet and Jacques MichauxKeywords: Chronology; Climatology; France; Mont-Hélène; Pliocene; RodentsAbstract The Mont-Hélène's fauna [Pyrénées-Orientales, France], includes 15 species of rodents with a new one, Occitanomys montheleni n. sp. among the 9 species of the Murids which are listed. The uncommon Cricetid, Blancomys neglectus, is well represented in the fauna. Peculiarities of the population referred to Slephanomys cf. donnezaniare discussed. The locality a fissure filling may be the oldest one of Tabianian age known in Southern France. The diversity of the Murids gives evidence of a subtropical climate and of a diversified environment which may be linked to the spreading of the coastal plain following the filling up of the Roussillon Neogene Basin. Article infos Published in Vol. 16, Fasc. 3 (1986) |
|
|

|
Crivadiatherium iliescui n. sp., nouvel Embrithopode (Mammalia) dans le Paléogène ancien de la dépression de Hateg (Roumanie).Constin Radulesco and Jean SudreKeywords: Embrithopods; Late Eocene; Paleobiogeography; RomaniaAbstract The investigations undertaken at Crivadia (Hateg Depression, Hunedoara District, Romania), the type locality of Crivadiatherium mackennai RADULESCO el al. (Radulesco, Iliesco et lliesco, 1976), led to the discovery of remains of a new Embrithopod. Close to the above mentioned species, but larger in size, this animal is here described as a new species of Crivadiatherium, C. iliescui. ln addition, the comparison made between the forms indicated above and Palaeaamasía kansui OZANSOY from the Eocene deposits of Anatolia (Ozansoy, 1966; Sen et Heintz, 1979) showed that the latter species included a heterogeneous material; this permitted us to distinguish the form in the Anatolian locality Ciçekdag-Arabin Kôyü under the name Palaeoamasia sp. The geographical distribution and diversity of the Embrithopod species under discussion (Balkan, Anatolia) support the idea of an eurasiatic origin of this group and seem to suggest the existence during the Eocene of a particular faunal province in south-eastern Europe. Article infos Published in Vol. 15, Fasc. 3 (1985) |
|
|
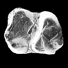
|
Nouvelles données sur les mammifères du Thanétien et de l'Yprésien du bassin d'Ouarzazate (Maroc) et leur contexte stratigraphique.Emmanuel Gheerbrant, Jean Sudre, Sevket Sen, Claude Abrial, Bernard Marandat, Bernard Sigé and Monique Vianey-LiaudKeywords: early Paleogene; magnetostratigraphy; Mammals; Morocco; North Africa; Ouarzazatz basin; SystematicsAbstract New faunal and stratigraphical data on the vertebrates localities from the early Paleogene of the Ouarzazate Basin (Adrar Mgorn 1, Adrar Mgorn 1 bis et N'Tagourt 2), Morocco, are presented. A magnetostratigraphical study, the first for such early Paleogene Arabo-African mammal localities, and the discovery of probable remains of the nannofossil Discoaster support the Thanetian age of the Adrar Mgorn 1 site. The magnetostratigraphy suggests a slightly later age than was thought for the Paleogene formations of the local series of Tinerhir and for the vertebrate localities: late or latest Thanetian for Adrar Mgorn 1 and Adrar Mgorn 1 bis, middle Ypresian for N'Tagourt 2. It also indicates a lower position of the KT boundary in the series. Two tons of matrix recovered in the vertebrate sites have vielded new data on the micromammals. A damaged lower molar from N'Tagourt 2 is referable to Khamsaconus bulbosus and supports the proboscidean affinities of this species and especially possible relationships with bunolophodont taxa such as elephantiforms. A lower molar from Adrar Mgorn 1 bis belongs to a new form which can be identified as a plesiadapiform or an euprimate close to Altiatlasius koulchii though significantly larger. A new material from Adrar Mgorn 1 illustrates a new dilambdodont adapisoriculid species which is referable to Garatherium : ?Garatherium todrae n. sp. Another species referred to Garatherium is known in the locality (?Garatherium n. sp.). Garatherium is a new lineage from the Ouarzazate basin which crosses the Paleocene-Eocene boundary together with Palaeoryctes, Didelphodontinae gen. and sp. 2, Todralestes, and Afrodon, and it is the first Paleocene-Eocene lineage identified outside of this basin (Garatheríum is based on a species from El Kohol, Algeria). Among the Paleocene-Eocene lineages from the Ouarzazate basin, it should be also mentioned a new possible carnassial form (carnivoran or creodont; Adrar Mgorn 1), and an upper molar of Cimolestes cf. incisus (Adrar Mgorn 1 bis). The upper molar THR 168 previously reported as from an indeterminate didelphodontine is here identified as the M1/ of Afrodon chleuhi. The micromammal faunas from the Ouarzazate basin are positioned in the global chronological framework of the mammal localities from the Paleogene of the Arabo-African domain. Article infos Published in Vol. 27, Fasc. 3-4 (1998) |
|
|

|
Acinoptèrygiens du Stéphanien de Montceau-les-Mines (Saône-et-Loire, France).Daniel Heyler and Cécile PoplinKeywords: Aeduelliforms; Biogeography; Palaeonisciforms; paramblypteriforms; StephanienAbstract The study of new specimens from the Stephanian shales of Montceau-les-Mines confirms and enlarges the number of groups already known in this area. Among the Palaeonisciforms, “form A" is now known more completely, although no diagnosis or name can yet be given for it. “Form B" is redescribed and its relationships with “Elonichthys robisoni" are discussed. A palaeoniscid is recorded which resembles those from Bourbon l'Archambault. The paramblypteriforms occur rather frequently, but no genera can be determined. The aeduelliforms comprise some specimens close to Aeduella blainvíllei from Muse (Autun basin), and a new genus. Comparison of the latter with two fossils from Lally allows creation of two new species and a new family. This diversification of the aeduelliforms during this middle Stephanian leads to the hypothesis that the group originated at least as early the lower Stephanian. This material prooves again the characteristic endemism of this fauna, particularly of the aeduelliforms which are known only in the Massif Central where they diversified during the Permo-Carboniferous. Biogeographical consequences are discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 13, Fasc. 3 (1983) |
|
|
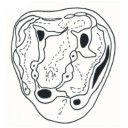
|
The beginning of the adaptive radiation of Theridomorpha (Rodentia) in Western Europe: morphological and phylogenetic analyses of early and middle Eocene taxa; implications for systematics
|
|
S.I. Data |
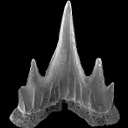
|
Two new scyliorhinid shark species (Elasmobranchii, Carcharhiniformes, Scyliorhinidae), from the Sülstorf Beds (Chattian, Late Oligocene) of the southeastern North Sea Basin, northern Germany.Thomas ReineckeKeywords: Chattian; Elasmobranchii; North Sea Basin; Scyliorhinidae; Scyliorhinusdoi: 10.18563/pv.38.1.e1 Abstract Based on isolated teeth two new scyliorhinid shark species, Scyliorhinus biformis nov. sp. and Scyliorhinus suelstorfensis nov. sp., are described from the Sülstorf Beds, early-middle Chattian, of Mecklenburg, northeastern Germany. They form part of a speciose assemblage of necto-benthic sharks and batoids which populated the warm-temperate to subtropical upper shelf sea of the south-eastern North Sea Basin. Article infos Published in Vol.38-1 (2014) |
|
|

|
Revision of the historical collections of Pliocene-Pleistocene large mammals from Le Riège and Saint-Palais localities, near Pézenas (Southern France)Federica Mulè, Luca Pandolfi, Anne-Lise Charruault, Jean-Yves Crochet, Jérôme Ivorra, Fabrice Lihoreau, Laurent Marivaux, Mehdi Mouana, Félix Nesme, Céline Robinet, Philippe Münch and Pierre-Olivier AntoineKeywords: Hérault; Mammalia; Montpellier; Neogene; Quaternarydoi: 10.18563/pv.48.1.e2 Abstract Numerous “Quaternary” large-mammal fossils have been collected since the 1830s along the Le Riège stream, near Pézenas (Southern France). More than 120 specimens are stored in the collections of the Université de Montpellier (UM) under the name “Le Riège”. A major operation aiming at relocating the palaeontological collections of the University has made it possible to group together all the specimens of interest and launch their systematic revision for the first time. The fossils belong to the Reboul (1839; 51 samples) and de Christol (1865; 18 samples) Collections and 17 samples compose the Crochet & Ivorra Collection (1998). The remaining 38 samples have no mention about the exact time and location of their finding. We provide a critical inventory with literal transcription of inscriptions on specimens and historical labels. This revision confirms the presence of two distinct faunal assemblages under the name of “Le Riège”: Saint-Palais (Early Pliocene, MN14–15) and Le Riège sensu stricto (late Early Pleistocene, most likely MNQ19). The former assemblage, with coastal affinities, is composed of the ruminants Alephis sp. and Procapreolus cf. pyrenaicus, the rhinocerotid Pliorhinus megarhinus, the gomphotheriid Anancus arvernensis and marine mammals, all emblematic taxa for the Early Pliocene of Montpellier and Perpignan. The latter assemblage documents a late Early Pleistocene fluvio-volcanic sequence, yielding the bovid Bison (Eobison) spp., the cervid Eucladoceros cf. giulii, the hippopotamid Hippopotamus antiquus, the rhinocerotid Stephanorhinus etruscus, the equid Equus cf. altidens, and the elephantid Mammuthus cf. meridionalis, plus a few specimens of uncertain taxonomic affinities. This revision underscores the interest of revisiting historical collections and further provides a starting point for future research. Article infos in press |
|
S.I. Data |