Print ISSN: 0031-0247
Online ISSN: 2274-0333
Frequency: biannual
stratigraphy and biochronology of Oligo-Miocene of Kazakhstan
Notidanodon tooth (Neoselachii: Hexanchiformes) in the Late Jurassic of New Zealand
Additions to the elasmobranch fauna from the upper Cretaceous of New Jersey (middle Maastrichtian, Navesink Formation)
Eocene otoliths (Clinchfield Formation), Georgia
Fossil snakes, Palaeocene, Itaborai, Brazil, Part I
Eocene (57) , Quercy Phosphorites (38) , Systematics (32) , Rodents (29) , Mammalia (27)

|
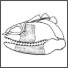
Designating a lectotype for Mesacanthus pusillus (Gnathostomata: Acanthodii)Matthew Baron and Kevin SeymourKeywords: acanthodians; Chordata; Devonian; Midland Valley; Orcadian Basindoi: 10.18563/pv.44.1.e2 Abstract The early gnathostome genus Mesacanthus is well represented in both Lower Old Red Sandstone and Middle Old Red Sandstone assemblages of northern and central Scotland. This ‘acanthodian’ taxon is currently thought to comprise two valid species: M. mitchelli and M. pusillus. Although the whereabouts of the holotype of M. mitchelli (NHMUK PV P560) is known, the syntype material for M. pusillus has long been thought lost. Here we identify at least one specimen that formed part of the original syntype material for M. pusillus, albeit in a slightly different condition than when it was originally figured. This specimen is ROM 25872, which is here designated as the lectotype. A second specimen – ELGNM 1978.191.1 – could represent another of the syntype specimens, but poor preservation quality makes it impossible to be certain. Article infos Published in 44-1 (2021) |
|
S.I. Data |
|
Description des restes d'Elasmobranches (Pisces) du Dévonien moyen de BoliviePhilippe JanvierKeywords: South AmericaAbstract Some fragmentary remains of spines and endoskeletal elements, referred here to as ctenacanthid like elasmobranchs, are recorded in the Middle Devonian of Bolivia. These specimens, and some others from the Eodevonian of Brasil represent the only Devonian fish remains hitherto known from South America and indicate that further discoveries may be made in their original localities respectively. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 4 (1977) |
|
|

|
Nouvelle interprétation de l'évolution du genre Megacricetodon au cours du MiocèneJean-Pierre AguilarKeywords: Megacricetodon; Micromammals; MioceneAbstract La découverte de nouveaux gisements à micromammifères dans le Miocène du Sud de la France et d'Espagne montre que, s'il n'est plus possible d'accepter dans son intégralité le schéma phylétique de Fahlbusch du genre Megacricetodon, il existe toutefois des segments de lignées à l'intérieur de provinces géographiques différentes (Péninsule Ibérique, France, Europe Centrale), avec lesquels on peut établir une biochronologie locale, segments qu'il est aussi possible de placer les uns par rapport aux autres, en utilisant les corrélations que l'on peut reconnaître entre certains niveaux repères des mammalogistes et l'échelle stratigraphique marine. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
La variabilité morphologique dentaire du Landenodon (Condylarthra) de Dormaal, (Eocène,Belgique)Marc GodinotKeywords: Condylarths; Dormaal; Early Eocene; LandenodonAbstract The study of dental variations in Landenodon from Dormaal (early Eocene, Belgium) shows that only one Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Koobi Fora Research Project, volume 3. The fossil ungulates: geology, fossil artiodactyls, and palaeoenvironments, édité par John Michael HARRIS, 1991. Clarendon Press, Oxford, xvi + 384 p. ISBN 0-19-857399-5.Jean SudreKeywords: Artiodactyls; palaeovenvironments; UngulatesAbstract Avec ce volume se clôture l'étude géologique et paléontologique des sites à hominidés de Koobi Fora. Il fait suite aux deux précédents ouvrages, parus respectivement en 1978 et 1983, consacrés également à l'étude des faunes recueillies sur ces gisements dans le cadre du Koobi Fora Research Project. Article infos Published in Vol. 22, Fasc. 2-3 (1993) |
|
|

|
The microfauna of the Djebel Qafze CaveG. HaasKeywords: Micromammals; RodentsAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 5 (1972) |
|
|

|
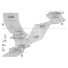
Contribution à la classification des Pistes de Vertébrés du Trias : les types du Stormberg d'Afrique du Sud (2 ème Partie: le Stormberg supérieur - 1. Le biome de la zone B/1 ou niveau de Moyeni: ses biocénoses).Paul EllenbergerKeywords: biocenosis; Footprints; South Africa; Stormberg; TriasAbstract Les Pistes de Vertébrés du Stormberg Supérieur ("Trias terminal à Rhétien"), ou Quthingien Article infos Published in Vol. 6, Ext (1974) |
|
|
|
Rates of evolution in divergent species lineages as a test of character displacement in the fossil record : tooth size in Paleocene Plesiadapis (Mammalia, Proprimates)Phillip D. GingerichKeywords: character displacement; character divergence; fractal time series; Plesiadapis; Rates of evolutionAbstract Two species lineages of North American late Paleocene Plesiadapis exhibit a pattern of size divergence from a common ancestral lineage. Time series of fossils in each of these lineages are analyzed to test the idea that size divergence represents competitive character displacement. The critical factor in a test of character divergence is showing that divergent lineages evolved directionally rather than randomly (multifactorially). Analysis of evolutionary rates and their temporal scaling in Plesiadapis shows that both divergent species lineages have the scaling slope expected for lineages evolving randomly rather than directionally, and size divergence in Plesíadapis does not represent character displacement. Rates of evolution commonly observed on a per-generation time scale are high enough to produce character displacement within a few generations. Thus character displacement is not likely to be visible on scales of time that can be studied in the fossil record. Article infos Published in Vol. 25, Fasc. 2-4 (1996) |
|
|

|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 10 - Paléothérides (Perissodactyles).Jean-Albert RemyKeywords: Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract La poche à phosphorite de Sainte-Néboule (Lot) a livré au cours des récentes campagnes de fouilles effectuées dans le cadre de la Rep 311 une douzaine de dents ou fragments de dents de paléothéridés à rapporter à 3 taxons. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
Les Ischyrictis de la transition Vindobonien-VallésienMiquel Crusafont i PairóKeywords: Ischyrictis; MustelidaeAbstract Abstract not available Article infos Published in Vol. 05, Fasc. 5 (1972) |
|
|
|
Premier signalement du Monachinae (Phocidae, Mammalia) dans le Sahélien (Miocène supérieur) d'Oran (Algérie)Christian de MuizonKeywords: Algeria; Late Miocene; PhocidaeAbstract Messiphoca mauretanica nov. gen., nov. sp. représente le premier Phocidae fossile recensé en Afrique du Nord. Provenant du gisement sahélien (Miocène supérieur) de Raz-el-Aïn (Algérie), il est connu par quelques os du membre antérieur (humérus, radius, ulna), quelques vertèbres dorsales et un crâne très fragmentaire. La description de cette forme nouvelle amène à considérer Messiphoca mauretanica comme un Monachinae archaïque proche de l'origine du groupe Pliophoca - Monachus. L'incidence de cette interprétation d'un Phocidae «pré-Messinien ›› sur la crise de salinité du Messinien est aussi envisagée. Article infos Published in Vol. 11, Fasc. 5 (1981) |
|
|

|
Premières données sur les rongeurs de la formation de Ch'orora (Ethiopie) d'âge Miocène supérieur. I: ThryonomyidésJean-Jacques Jaeger, Jacques Michaux and Maurice SabatierKeywords: Ethiopia; Paraulacodus; Rodents; Upper MioceneAbstract The genus Paraulacodus has been collected in the Ch'orora formation of Upper Miocene age, in Ethiopia. The new species, P. johanesi n. sp.. is more evolved than the previously described indian species P. indicus HINTON of the Siwalik Hills area. The morphological gap between P. johanesi and the present Thryonomys is still important. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Essai de filiation des campagnols et des lemmings (Arvicolidae, Rodentia) en zone holartique d'après la morphologie dentaire.Jean ChalineKeywords: Arvicolidae; Dental morphology; Paleogeography; phyletic relationshipsAbstract The Arvicolid evolution results in an increase of the dental structure complexity. The M3/ differenciation seems to characterise the tribe subdivisions, that of M/1 being variable from one to another lineage. The phyletic relationships of fossil lineages are discussed from a paleogeographic point of view. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|
|
Découverte d'un gisement de micromammifères d'âge Pliocène dans le bassin de Constantine (Algérie), présence d'un muridé nouveau : Paraethomys Athmeniae n.sp.Brigitte Coiffait and Philippe-Emmanuel CoiffaitKeywords: Algeria; Constantine; Micromammals; Muridae; PlioceneAbstract The study of that locality allowed the description of a new Muridae : Paraethomys athmeniae n. sp. It reveals the existence of new rodent for Algeria : first, a Sciuridae, Atlantoxerus cf. rhodius, and second, a Gliridae, Eliomys truci. So, that work shows the presence of the genus Eliomys in North Africa before the middle of Pleistocene. Lastly, Paraethomys cf. anomalus gives an exact datation of that bed. Article infos Published in Vol. 11, Fasc. 1 (1981) |
|
|

|
Table ronde sur les phosphorites du Quercy Montauban 15-16 Décembre 1972Louis Thaler and Jean-Louis HartenbergerKeywords: Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract Voici une centaine d'années débutait sur les Causses du Quercy l'exploitation des phosphorites qui devait permettre d'amasser des collections de Vertébrés fossiles uniques au monde. Ces fossiles firent l'objet de nombreuses publications et les noms de Filhol, Gaudry, Schlosser, Stehlin, Teilhard de Chardin sont attachés à ces premières études. Article infos Published in Vol. 06, Fasc. 1-2 (1974) |
|
|

|
Le genre Microstonyx en Espagne et ses relations avec les autres espèces du même genre hors d'EspagneJuana M. Golpe-PosseKeywords: Microstonyx; Spain; SuidaeAbstract The genus Microstonyx was found only in the north eastern part of Spain : M. antiquus, referable to the Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Problems of classification as applied to the RodentiaAlbert E. WoodKeywords:Abstract A classification should be both usable and useful,not too complex either in the amount of splitting or in the number of hierarchies involved, and not so simple as to give a false assurance of knowledge of relationships. Classifications are only possible because we do not have complete knowledge of the evolution of the organisms concerned because gaps in the record are necessary to allow the separation of the various taxa. Rodent classification is complicated by the large number of organisms involved and by the geat amount of parallelism that has taken place in the evolution of any and all features. If several independent features are characteristic of a certain taxon, should an effort be made to define the group on the basis of all the features, or should only one be selected as the determinant ? Unless the evolution of the several features was closely linked, the former solution will sooner or later lead to insurmountable problems. Article infos Published in Vol. 9, Ext (1980) |
|
|

|
Rongeurs (Mammalia, Rodentia) du Miocène de Beni-MellalJean-Jacques JaegerKeywords: Morocco; NeogeneAbstract The rodent fauna of Beni-Mellal is characterized by the abundance of ctenodactylids and cricetids. The latter are represented by four distinct species, among which a new form. Dakkamys zaiani nov. gen., nov. sp. is described. A detailed morphological analysis shows that, contrary to that which had been established before, « Cricetodon ›› atlasi Lavocat, 1961, is not closely related to any European form known; this species is attributed, in consequence, to the new genus Mellalomys. A simple biometric analysis has shown that the genus Myocricetodon Lavocat, 1952, is represented in this locality by two distinct species. The systematic homogeneity of the Beni-Mellal cricetids is also demonstrated: they can, as a matter of fact, all be referred to the subfamily Myocricetodontinae. The definition of this subfamily is completed. The sciurids and glirids are also reviewed in the light of new systematic and biogeographic information established ln Europe. A new species of Atlantoxevus from the early Pleistocene of Morocco, A. huvelini nov. sp., is described. It is probably the descendant of A. tadlae from Beni-Mellal. Biogeographic analysis leads one to consider this fauna as the result of geographic isolation in the Maghreb since the late Oligocene or the early Miocene. In particular no direct European influence can be discerned. Stratigraphic considerations resulting from the discovery of new localities in North Africa lead to the confirmation of the ante-Vallesian age of this fauna and to its parallelism with the faunas of La Grive in Western Europe and Fort Ternan in East Africa. The peculiar geologic nature of this locality is discussed. Article infos Published in Vol. 07, Fasc. 4 (1977) |
|
|
|
La poche à phosphate de Ste-Néboule (Lot) et sa faune de vertebres du Ludien supérieur. 11- CréodontesBrigitte Lange-BadréKeywords: Creodonta; Eocene; Quercy PhosphoritesAbstract The teeth and the astragale of the Creodonta from Ste-Néboule (Lot) are referred to Hyaenodon brachyrhynchus. Isolated teeth fit morphologically the material from La Débruge (Middle Ludian). However, biometric analysis suggests an Upper Ludian age. Article infos Published in Vol. 08, Fasc. 2-4 (1978) |
|
|
|
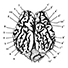
Etude paléoneurologique comparative de Parabos Cordieri (De Christol), un bovidae (Mammalia, Artiodactyla) du Pliocène d'Europe Occidentale.Catherine GromolardKeywords: Bovidae; endocranial cast; Europe; PlioceneAbstract A skull of Parabos cordieri, undamaged by fossilisation, allows us to make an endocranial cast, which is compared to those of Bos taurus, Boselaphus tragocamelus and Hippotragus equinus. These are studied by general form (shape, volume, « rolling-up›› and inclination), and by detailed morphology (gyri and sulci patterns, rete mirabile, importance of rhinencephalon and cerebellum). Article infos Published in Vol. 12, Fasc. 2 (1982) |
|